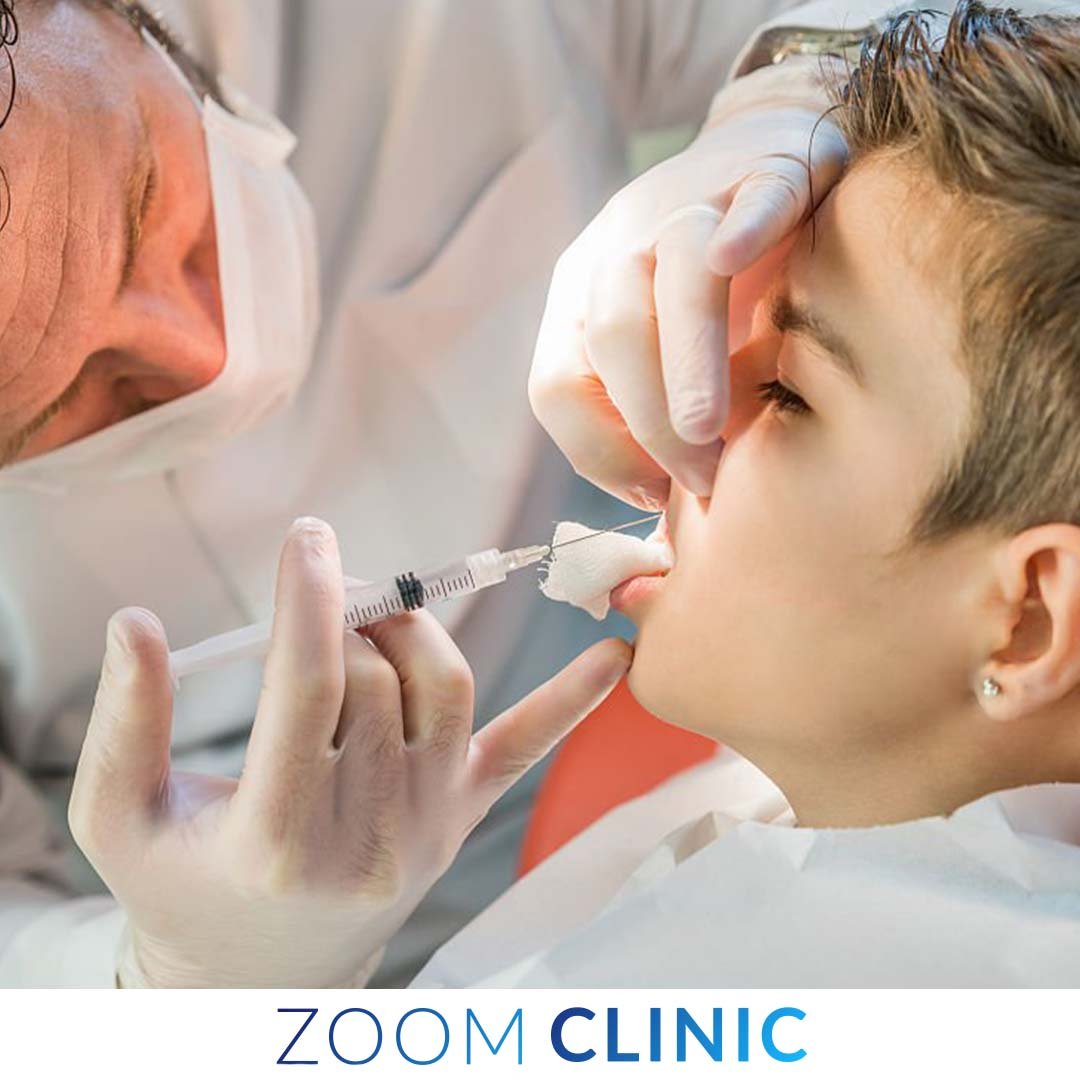
In dentistry, patient comfort and pain management have become paramount. Advances in modern anesthesia techniques for a pain-free experience have revolutionized dental care, ensuring that patients can undergo dental procedures without fear and discomfort.
This article explores various modern anesthesia techniques and their impact on dental procedures, patient safety, and overall satisfaction.
Table of content
Understanding Dental Anesthesia
Dental anesthesia is essential for providing pain relief during dental procedures. It allows dental professionals to perform complex procedures without causing discomfort to the patient.
Several types of dental anesthesia are available, including local anesthesia, sedation, and general anesthesia, each serving different purposes depending on the procedure and patient needs.
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is the most common form of anesthesia used in dental practices. It involves injecting a local anesthetic agent to numb a specific area of the mouth.
Regional anesthesia provides profound anesthesia and ensures that the patient does not feel pain during the procedure. Some common local anesthetics used in dental procedures include lidocaine, articaine, and bupivacaine.
Techniques for Administering Local Anesthesia
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block: This technique numbs the lower jaw and is commonly used for procedures involving the lower teeth.
- Infiltration Anesthesia: This method involves injecting the anesthetic solution directly into the tissue near the area being treated. It is commonly used for upper teeth and soft tissues.
- Topical Anesthetic Agents: Before the injection, a topical anesthetic gel can be applied to the injection site to reduce pain and discomfort from the needle insertion.
Sedation Dentistry
Sedation dentistry involves using soothing agents to help patients relax during dental procedures. It is beneficial for patients with dental anxiety or those undergoing lengthy or complex procedures.
Sedation can range from minimal sedation, where the patient is relaxed but awake, to deep sedation, where the patient is on the edge of consciousness.
- Nitrous Oxide (Laughing Gas) is a safe and effective sedative agent that is inhaled through a mask. It helps reduce anxiety and pain while allowing the patient to remain conscious.
- Oral Sedation: Involves taking a sedative pill before the procedure to induce relaxation.
- Intravenous (IV) Sedation: Administered directly into the bloodstream for a deeper level of sedation.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is used for more complex procedures or patients with severe dental anxiety. It involves rendering the patient completely unconscious.
This type of anesthesia is typically administered by an anesthesiologist in a hospital or specialized dental office setting.
Modern Techniques and Innovations in Dental Anesthesia
Recent advancements in dental anesthesia have focused on improving patient comfort, safety, and the effectiveness of pain relief. Here are some modern techniques and innovations:
Computer-Controlled Local Anesthesia Delivery
Computer-controlled local anesthesia delivery systems, such as The Wand, provide a steady and precise flow of anesthetic, reducing the discomfort associated with traditional injections.
This technique enhances patient comfort by minimizing injection pain and anxiety.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS is a non-invasive method that uses low-voltage electrical currents to alleviate pain. It works on the gate control theory, which suggests that electrical stimulation can block pain signals from reaching the brain. TENS can be used in conjunction with local anesthesia to provide additional pain relief.
Anesthetic Buffering
Anesthetic buffering involves adjusting the pH of the local anesthetic solution to make it more comfortable for the patient. By reducing the acidity of the anesthetic, the injection is less painful, and the onset of anesthesia is quicker.
Intraosseous Anesthesia
Intraosseous anesthesia involves injecting the anesthetic directly into the bone surrounding the tooth. This technique provides immediate and profound anesthesia, making it ideal for procedures that require deep numbing.
Ensuring Patient Safety and Comfort
The primary goal of modern anesthesia techniques is to ensure patient safety and comfort. Dental professionals are trained to evaluate each patient’s medical history and specific needs to determine the most appropriate anesthesia method.
Evaluating Patient’s Medical History
Before administering any form of anesthesia, dental practitioners review the patient’s medical history to identify any potential risks or contraindications.
This includes checking for allergies to anesthetic agents, assessing overall health, and understanding any previous adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Patient Education and Communication
Effective communication between the dental team and the patient is crucial for a successful and pain-free experience. Patients are informed about the anesthesia process, potential side effects, and what to expect during and after the procedure.
This helps reduce anxiety and builds trust between the patient and the dental professionals.
Postoperative Care and Pain Management
Postoperative care is essential for managing pain and ensuring a smooth recovery. Patients are provided with clear instructions on how to care for the treated area, including guidelines on pain management, oral hygiene, and any necessary medications.
Addressing Dental Anxiety
Dental anxiety is a common issue that can prevent individuals from seeking necessary dental care. Modern anesthesia techniques play a vital role in alleviating this anxiety and making dental visits more manageable.
Creating a Relaxing Environment
Dental offices are increasingly focused on creating a relaxing and welcoming patient environment. This includes comfortable waiting areas, soothing music, and a friendly, compassionate dental team.
Offering Sedation Options
By offering various sedation options, dental practices can cater to patients with different levels of anxiety. Patients can choose the option that best suits their comfort level, from mild sedation with nitrous oxide to deeper sedation with IV sedation.
Special Considerations for Pediatric and Special Needs Patients
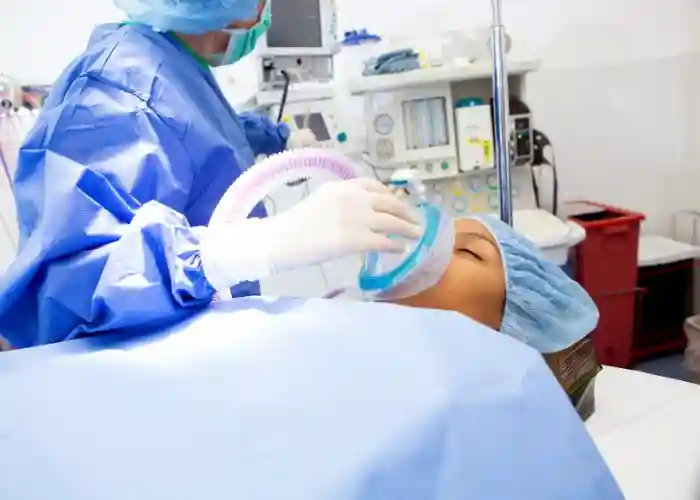
Children and patients with special needs require particular attention and care regarding dental anesthesia. Pediatric patients, in particular, may have a heightened fear of dental procedures and require techniques tailored to their needs.
Pediatric Anesthesia
Pediatric patients often benefit from a combination of topical anesthetics and nitrous oxide to help them relax and reduce pain.
Dental professionals specializing in pediatric dentistry are trained to manage the unique challenges of treating young patients.
Special Needs Dentistry
For patients with special needs, personalized care plans are developed to address their specific requirements. This may include sedation, general anesthesia, and additional support from caregivers or family members.
Advancements in Anesthesia Research and Development
Ongoing research and development in dental anesthesia continue to improve the techniques and agents available to dental professionals.
Innovations in anesthetic formulations, delivery methods, and patient monitoring pave the way for even safer and more effective pain management solutions.
Clinical Trials and Studies
Clinical trials and studies play a crucial role in advancing dental anesthesia. Researchers continually explore new anesthetic agents and delivery systems to enhance patient comfort and safety.
Collaboration with Medical Professionals
Collaboration between dental practitioners and other medical professionals, such as anesthesiologists and pain specialists, helps ensure the best possible outcomes for patients.
This multidisciplinary approach allows for comprehensive care and the development of innovative pain management strategies.
Conclusion
Modern anesthesia techniques for a pain-free experience have transformed the landscape of dental care. With advancements in local anesthesia, sedation dentistry, and general anesthesia, patients can undergo dental procedures with minimal discomfort and anxiety.
By focusing on patient safety, comfort, and effective pain management, dental professionals can provide high-quality care that meets the needs of diverse patient populations.
Understanding and utilizing these modern techniques enhances patient satisfaction and contributes to better oral health outcomes.
As research and development continue to drive innovation in dental anesthesia, the future of pain-free dental care looks promising, ensuring patients receive the treatment they need without fear or discomfort.
Dental practices can build trust and foster a positive patient experience by prioritizing patient education, effective communication, and personalized care.
Modern anesthesia techniques are vital in achieving a pain-free and successful dental experience, whether addressing dental anxiety, managing complex procedures, or providing specialized care for pediatric and special needs patients.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
FAQs
These FAQs address common concerns and questions about modern anesthesia techniques in dentistry, providing patients with valuable information and reassurance for their dental procedures.
1. What are the different types of dental anesthesia?
The different types of dental anesthesia include local anesthesia, sedation (such as nitrous oxide, oral sedation, and IV sedation), and general anesthesia. Each type serves different purposes and is selected based on the procedure and patient needs.
2. How does local anesthesia work?
Local anesthesia blocks nerve signals in a specific mouth area, preventing pain during dental procedures. It is administered via injection and provides numbness in the targeted area.
3. What is the difference between local anesthesia and sedation?
Local anesthesia numbs a specific part of the mouth, allowing the patient to remain conscious but pain-free. On the other hand, sedation relaxes the patient and can range from minimal sedation, where the patient is awake but relaxed, to deep sedation, where the patient is on the edge of consciousness.
4. Is dental anesthesia safe?
Dental anesthesia is generally safe when administered by trained dental professionals. They assess the patient’s medical history and current health condition to ensure the appropriate anesthetic is used and monitor the patient throughout the procedure.
5. How can I reduce pain from the injection itself?
To reduce pain from the injection, dental professionals may use a topical anesthetic gel to numb the injection site before administering the local anesthetic. Techniques such as slow and steady injection and computer-controlled delivery systems can minimize discomfort.
6. What is nitrous oxide, and how is it used in dentistry?
Nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, is a soothing agent inhaled through a mask. It helps reduce anxiety and pain during dental procedures while keeping the patient conscious. It is safe and effective, providing a relaxed and comfortable experience.
7. Who might need general anesthesia for dental procedures?
General anesthesia is typically used for patients undergoing complex dental procedures, those with severe dental anxiety, or patients with special needs who may not be able to remain still or cooperative during the treatment.
8. What is TENS, and how does it help with dental pain?
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive method that uses low-voltage electrical currents to block pain signals. It can be used in conjunction with local anesthesia to provide additional pain relief during dental procedures.
9. How do dental professionals ensure patient safety during anesthesia?
Dental professionals ensure patient safety by reviewing the patient’s medical history, selecting the appropriate anesthetic, and monitoring the patient throughout the procedure. They also provide clear postoperative care instructions to manage pain and promote healing.
10. Can children receive dental anesthesia?
Yes, children can receive dental anesthesia. Pediatric dentists often use a combination of topical anesthetics and nitrous oxide to help young patients relax and reduce pain. The safety and dosage are carefully adjusted for pediatric patients.
11. What are the side effects of dental anesthesia?
Common side effects of dental anesthesia include temporary numbness, mild swelling at the injection site, and, occasionally, minor bruising. More severe side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions, which is why a thorough medical history is taken before administration.
12. How long does the numbness last after local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia’s numbness typically lasts 1 to 3 hours after the procedure. The exact duration can vary depending on the type of anesthetic used and the specific area treated.
13. What should I do if I experience anxiety about dental procedures?
Discuss your concerns with your dentist if you experience anxiety about dental procedures. They can offer various sedation options, such as nitrous oxide or oral sedation, to help you relax. Creating a calm and comfortable environment can also significantly reduce anxiety.
14. How can I prepare for a dental procedure involving anesthesia?
To prepare for a dental procedure involving anesthesia, follow your dentist’s pre-procedure instructions, which may include fasting for a certain period if general anesthesia or deep sedation is involved. Arrive at the appointment with a clear understanding of the procedure and any questions you may have.
15. What should I expect after receiving dental anesthesia?
After receiving dental anesthesia, you can expect temporary numbness and possibly mild discomfort at the injection site. Follow your dentist’s postoperative care instructions, which may include avoiding certain foods and activities until the numbness wears off.
16. Can dental anesthesia cause allergic reactions?
While rare, allergic reactions to dental anesthesia can occur. It’s important to let your dentist know of any known allergies or past reactions to medications. Your dentist will review your medical history to minimize the risk of an allergic reaction.
17. Are there alternatives to traditional anesthetic injections?
Yes, alternatives to traditional anesthetic injections include computer-controlled local anesthesia delivery systems like The Wand, which provide a steady and precise flow of anesthetic, reducing discomfort. Topical anesthetics and TENS are also alternative methods for pain management.
18. How does sedation dentistry help with dental anxiety?
Sedation dentistry helps with dental anxiety by using sedative agents to relax the patient. This can range from mild sedation with nitrous oxide to more profound sedation with oral or IV sedatives. Sedation dentistry makes it easier for anxious patients to receive necessary dental care.
19. What is the role of a dental anesthesiologist?
A dental anesthesiologist is a specialized dental professional trained in administering anesthesia. They ensure patient safety and comfort during complex dental procedures, particularly those requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation.
20. How do modern anesthesia techniques improve patient comfort?
Modern anesthesia techniques improve patient comfort by reducing pain and anxiety associated with dental procedures. Advances such as computer-controlled delivery systems, topical anesthetics, and TENS provide more precise and effective pain management, leading to a better overall experience.
Read Also
Can Anyone Get Dental Implants? Eligibility and Considerations