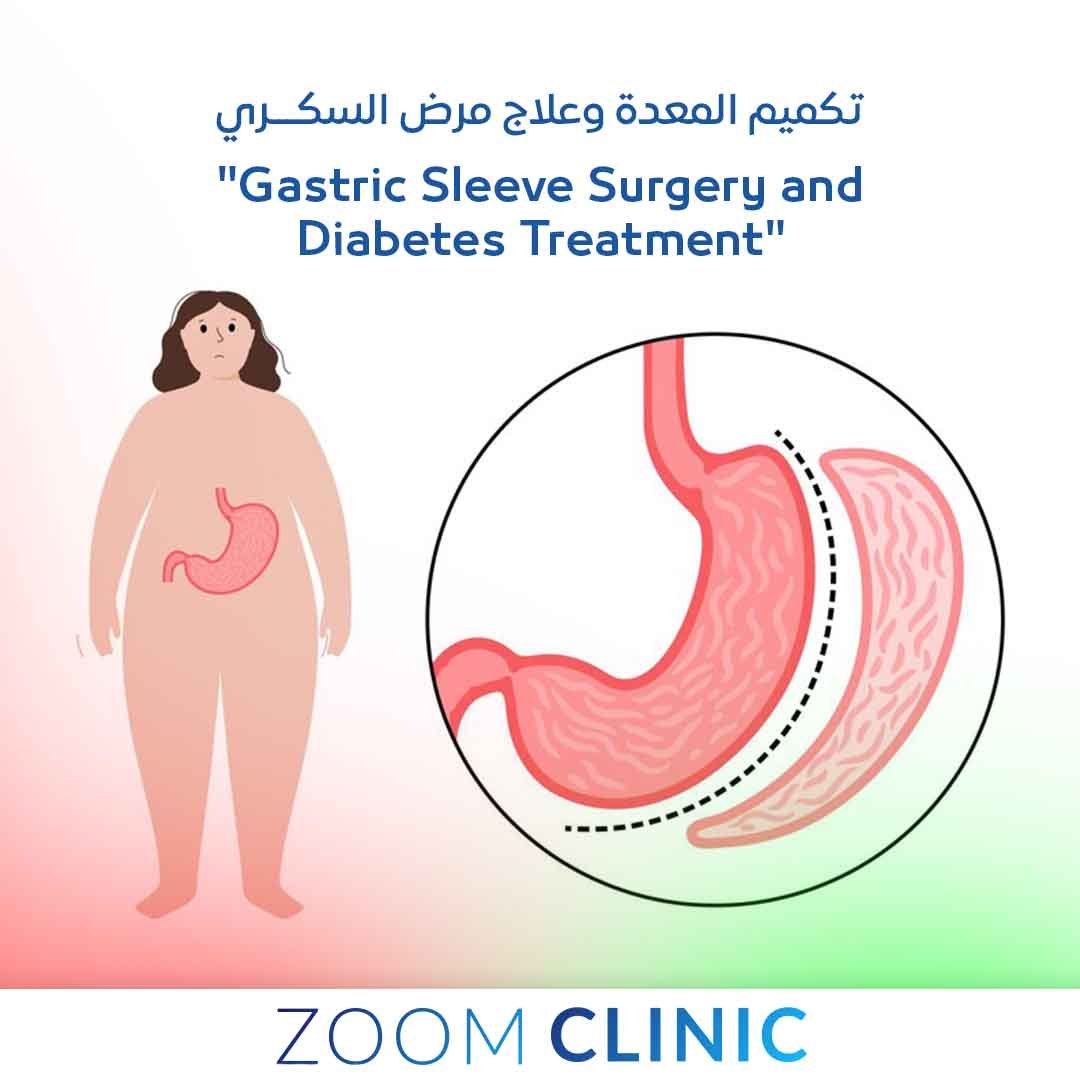
Gastric sleeve surgery is a bariatric surgery designed to promote weight loss by reducing stomach size, leading to decreased caloric intake.
Increasingly, this surgical procedure has shown promising outcomes in managing diabetes mellitus, particularly in obese patients who haven’t achieved control through traditional medical treatments.
The American Diabetes Association and other health organizations have highlighted the potential of such surgeries to improve diabetes remission rates and enhance overall clinical outcomes.
This article will explore the role of gastric sleeve surgery and similar metabolic surgeries in treating T2D, discussing the mechanism, benefits, and considerations involved.
Table of content
Understanding Gastric Sleeve Surgery
The gastric sleeve, or sleeve gastrectomy, involves removing a significant portion of the stomach, leaving a sleeve-shaped pouch that limits food intake.
The reduction in stomach size affects gut hormones linked to hunger and blood sugar regulation, making it particularly beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.

Unlike other bariatric procedures like gastric bypass or duodenal switch, sleeve gastrectomy does not alter the small intestine’s structure, thus minimizing complications associated with nutrient malabsorption.
Key Benefits of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
- Reduced Body Weight: Sleeve gastrectomy often results in significant weight loss, directly impacting insulin resistance and glycemic control.
- Hormonal Changes: The procedure modifies gut hormones such as ghrelin, reducing hunger and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
- Improved Diabetes Outcomes: Many patients experience reduced reliance on diabetes medications or remission following surgery.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of health problems if left untreated or poorly managed. It is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet, and is more common in people with a family history of the condition.
In type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels, or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Bariatric surgery, including gastric bypass surgery and sleeve gastrectomy, has been shown to be an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes in obese patients. These metabolic surgeries can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and even lead to remission of the disease in some cases.
In fact, studies have shown that bariatric surgery can be more effective than traditional medical obesity treatment in improving glycemic control and reducing cardiovascular risk factors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, bariatric surgery can also help reduce the need for diabetes medications and improve overall quality of life.
Overall, type 2 diabetes is a serious health condition that requires prompt treatment and management to prevent long-term complications. Bariatric surgery, including gastric bypass surgery and sleeve gastrectomy, is a viable treatment option for obese patients with type 2 diabetes, and can help improve glycemic control, reduce cardiovascular risk factors, and improve overall health outcomes.
Mechanism of Diabetes Control in Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Hormonal Impact
One primary mechanism by which gastric sleeve surgery aids in diabetes care is by altering gut hormones.
Reduced levels of ghrelin and increased levels of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) help improve blood glucose levels and insulin sensitivity, which is particularly valuable for morbidly obese subjects with diabetes.
Insulin Sensitivity and Weight Loss
The procedure’s significant weight reduction effect improves glucose metabolism and reduces insulin resistance.
The connection between body weight and insulin resistance means that losing weight directly correlates with improved blood sugar levels, making it easier for patients to manage or reverse diabetes.
Clinical Evidence: Gastric Sleeve and Diabetes Outcomes

Various randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and clinical trials have provided evidence of the effectiveness of gastric sleeve surgery for diabetes remission.
Studies like the SLEEVEPASS randomized clinical trial have compared outcomes between sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass surgery, focusing on diabetes remission, weight loss, and health benefits.
Key Findings from Clinical Trials
- Weight Loss and Diabetes Remission: Many bariatric surgery patients achieve significant weight loss and diabetes remission within the first few years following surgery.
- Improved Glycemic Control: Patients undergoing sleeve gastrectomy often experience better glycemic control than those relying on conventional diabetes medications.
- Reduced Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Weight loss and improved glucose metabolism reduce cardiovascular risk factors associated with T2D, like hypertension and high cholesterol.
Comparing Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass for Diabetes Treatment
Both gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgeries are highly effective, yet they have different implications for diabetes treatment.
Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Involves rerouting the small intestine, impacting nutrient absorption and hormonal regulation.
- Results in faster diabetes remission but may carry a higher risk of malnutrition.
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
- Reduces the stomach size but maintains the gastrointestinal tract’s natural flow, minimizing nutrient malabsorption.
- Provides sustainable weight loss and hormonal benefits with fewer long-term complications.
The Role of Body Mass Index in Bariatric Surgery Decisions
Body Mass Index (BMI) is crucial in determining the suitability of bariatric surgery for diabetes patients.
For individuals with a BMI over 35 who also suffer from T2D or other obesity-related comorbidities, metabolic surgery is often recommended.
Studies have shown that patients with higher BMIs tend to have more severe obesity and benefit the most from surgical procedures due to the associated weight loss and metabolic changes.
The Impact of Gastric Sleeve Surgery on Cardiovascular Risk Factors

Cardiovascular risk factors are often linked with T2D, with obesity playing a central role. Gastric sleeve surgery impacts multiple cardiovascular risk factors, as weight loss contributes to reductions in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart disease risk.
By helping patients lose weight and improve blood glucose control, gastric sleeve surgery provides dual benefits for diabetes and cardiovascular health.
Long-Term Diabetes Remission and Weight Regain
While many patients achieve diabetes remission after gastric sleeve surgery, maintaining this status over time can be challenging, especially if weight regain occurs.
Studies on long-term medical complications of weight loss surgery highlight the importance of sustained weight reduction and lifestyle changes in maintaining glycemic control.
Adopting healthy eating habits and regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential in sustaining the benefits of bariatric and metabolic surgery.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Obesity and T2D are commonly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can progress to severe liver conditions.
Weight reduction through sleeve gastrectomy has shown promising results in improving NAFLD markers.
Studies demonstrate that bariatric surgery patients frequently exhibit reduced liver fat and improved liver function, contributing to better overall health outcomes.
Considerations and Risks Associated with Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Though highly effective, gastric sleeve surgery carries some risks:
Surgical Risks: Potential complications include infection, blood clots, and leakage from the staple line.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Though less than with gastric bypass, patients may still require supplements.
Implant Failure and Weight Regain: Post-surgery, some patients may experience weight regain, affecting diabetes outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes: Success requires a commitment to healthy eating, regular exercise, and periodic medical check-ups.
The Importance of Intensive Medical Therapy
While gastric sleeve surgery is effective, some patients benefit from intensive medical therapy and surgical treatment.
Medications such as insulin or metformin may be needed initially to support glycemic control until the body adjusts post-surgery.
Combining surgical and medical approaches often improves clinical outcomes in patients with complex cases of T2D.
Randomized Clinical Trials and Their Findings

Various randomized clinical trials have contributed to our understanding of gastric sleeve surgery for diabetes, including:
The SLEEVEPASS Trial: Compared sleeve gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in terms of weight loss and diabetes remission, showing comparable benefits for T2D management.
Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) Study: One of the longest studies on bariatric surgeries and T2D, demonstrating sustained diabetes remission rates and reduced cardiovascular events.
These studies underscore the potential of bariatric metabolic surgery to provide long-lasting health improvements beyond traditional medical treatments.
Health Benefits Beyond Diabetes Remission
In addition to diabetes care, gastric sleeve surgery provides additional health benefits that enhance the overall quality of life, including:
- Improved Mobility: Weight loss helps with physical activity and reduces joint pain.
- Enhanced Respiratory Health: Many patients experience relief from sleep apnea and other respiratory issues.
- Psychological Benefits: Achieving a healthier body weight can boost self-esteem and mental well-being.
The Role of the American Diabetes Association
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recognizes the effectiveness of bariatric and metabolic surgery for treating T2D in patients with morbid obesity.
The ADA’s guidelines support using bariatric procedures like gastric sleeve surgery to improve diabetes outcomes and metabolic health.
Following these guidelines, healthcare providers increasingly recommend metabolic surgery as an essential tool for diabetes management in specific patient groups.
Potential Risks and Complications of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
While the benefits are clear, there are potential risks associated with gastric sleeve surgery, such as:
Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications: Some patients, especially those with severe obesity and long-term diabetes, may experience complications involving small and large blood vessels.
Weight Regain: A significant challenge, weight regain can compromise glycemic control and negate diabetes remission.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Although the gastric sleeve preserves the digestive pathway, nutritional deficiencies may still occur, particularly in iron, calcium, and vitamin B12.
Follow-Up Care and Lifestyle Changes Post-Surgery
Achieving and maintaining the full benefits of gastric sleeve surgery for diabetes management requires commitment:
Regular Check-Ups: Scheduled follow-ups with healthcare providers help monitor glycemic control, manage medications and blood pressure, manage nutrient intake, and adjust any ongoing treatments.
Healthy Eating Habits: It is crucial to embrace balanced eating habits. Focus on protein, fiber, and nutrient-dense foods to support healing, prevent weight regain, and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps maintain weight loss, and contributes to overall well-being.
Mental Health Support: Lifestyle changes post-surgery can be challenging. Psychological support and counseling can help manage expectations and maintain motivation.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
اقرأ أيضا:
Who Is Eligible for Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Reason for Weight Loss after Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Abdominal Changes After Sleeve Gastrectomy
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main goal of gastric sleeve surgery for diabetes?
Gastric sleeve surgery helps reduce body weight and improve insulin sensitivity, leading to better glycemic control. For many, it provides a path to diabetes remission. Additionally, this surgical procedure can significantly decrease the need for ongoing diabetes medications, enhancing the overall quality of life for patients. The combination of weight loss and improved metabolic health contributes to long-term success in managing type 2 diabetes.
Is gastric sleeve surgery effective for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, studies indicate high diabetes remission rates for type 2 diabetes after gastric sleeve surgery, especially when patients adhere to lifestyle changes post-surgery. The procedure not only aids in significant weight loss but also enhances metabolic health, making it a viable option for many. Furthermore, the hormonal changes that occur post-surgery contribute to improved glycemic control, reinforcing the benefits of this surgical approach in managing diabetes effectively.
Are there risks with gastric sleeve surgery?
Yes, potential risks include nutrient deficiencies, infection, and in rare cases, weight regain. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers helps mitigate these risks. Additionally, patients must be vigilant about maintaining nutritional intake and adhering to prescribed supplements to prevent deficiencies. It is crucial to have a comprehensive support system in place to address any complications and ensure long-term success.
How does gastric sleeve surgery impact cardiovascular health?
Weight loss following gastric sleeve surgery often reduces cardiovascular risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation, positively impacting heart health. This reduction in risk factors not only enhances cardiovascular function but also contributes to a decreased risk of developing further complications associated with type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the improvement in overall metabolic health supports better long-term outcomes for patients undergoing this procedure.
Who is a good candidate for gastric sleeve surgery?
Candidates typically have a BMI over 35 and obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes. They may also have tried and failed with conventional weight loss methods, highlighting the need for surgical intervention. A consultation with a bariatric specialist is essential to determine suitability, as they can assess individual health needs and potential benefits of the surgery.