Understanding the Procedure, Outcomes, and Long-Term Implications
Bariatric surgery has become an increasingly popular solution for individuals struggling with severe obesity and related health conditions. Among the various options available, Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass are two of the most commonly performed procedures.
However, there are instances where a patient who has undergone Sleeve Gastrectomy may require a Gastric Bypass surgery as a secondary or revisional procedure.
This comprehensive guide explores the reasons for considering Gastric Bypass after Sleeve Gastrectomy, the procedure itself, and the long-term outcomes for patients.
Table of content
What is Sleeve Gastrectomy?
Overview of Sleeve Gastrectomy
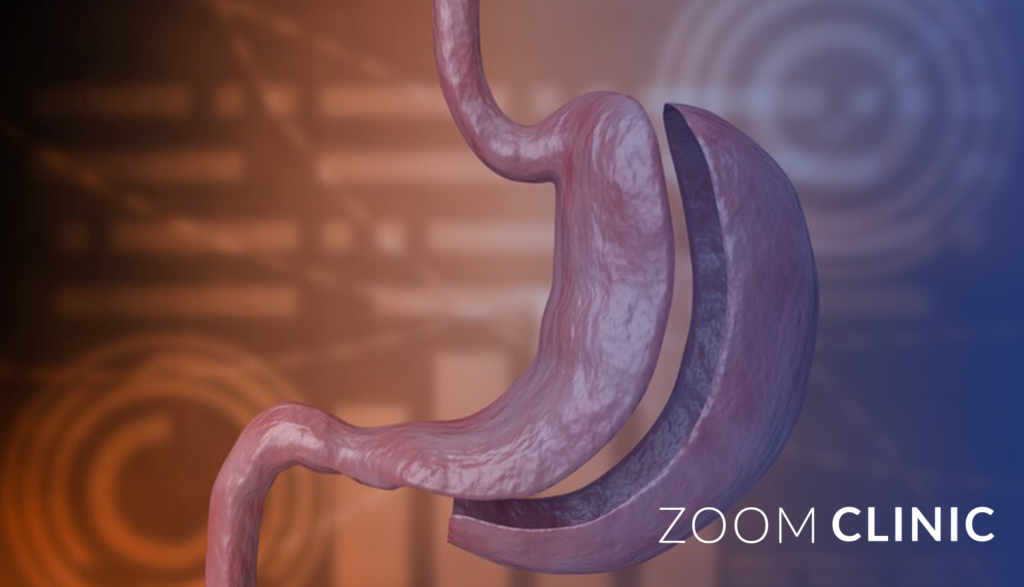
Sleeve Gastrectomy, also known as vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG), is a surgical weight-loss procedure that involves the removal of approximately 80% of the stomach.
This creates a smaller, tube-like stomach, or “sleeve,” which limits the amount of food that can be consumed at one time. The surgery also reduces the production of the hunger hormone ghrelin, which can help decrease appetite.
Benefits of Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Significant Weight Loss: Sleeve gastrectomy can result in substantial weight loss, often leading to the resolution or improvement of obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
- No Bypassing of the Intestines: Unlike Gastric Bypass, Sleeve Gastrectomy does not involve rerouting the intestines, which reduces the risk of certain complications such as malabsorption of nutrients.
- Simplicity of Procedure: Sleeve gastrectomy is generally considered a simpler procedure than Gastric Bypass, with a shorter operative time and fewer potential complications.
Limitations and Potential Complications
While Sleeve Gastrectomy is highly effective for many patients, it is not without its limitations. Some individuals may experience insufficient weight loss or weight regain after the procedure.
In addition, complications such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), strictures, or inadequate resolution of comorbidities may arise. In these cases, a secondary procedure, such as Gastric Bypass, may be considered.
Why Consider Gastric Bypass After Sleeve Gastrectomy?
Indications for Revisional Surgery
There are several reasons why a patient who has undergone Sleeve Gastrectomy might consider Gastric Bypass as a secondary procedure:
1. Insufficient Weight Loss or Weight Regain
While Sleeve Gastrectomy is effective for many patients, some may experience less than optimal weight loss or may regain weight after the initial surgery. Factors such as diet, lifestyle habits, and individual metabolic responses can influence long-term weight outcomes. For patients who have not achieved their weight loss goals or who have regained a significant amount of weight, Gastric Bypass may offer a more aggressive solution.
2. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a common complication after Sleeve Gastrectomy. The reduction in stomach size and alteration in anatomy can lead to increased acid reflux and heartburn. In some cases, GERD may become severe and unresponsive to medication, leading patients to seek a revisional surgery. Gastric Bypass is known to be highly effective in resolving GERD, as it reroutes the stomach and intestines, reducing acid production and reflux.
3. Inadequate Resolution of Comorbidities
For some patients, Sleeve Gastrectomy may not adequately resolve obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension. Gastric Bypass, with its more significant impact on hormonal regulation and nutrient absorption, can provide better resolution of these conditions.
4. Mechanical Complications
Mechanical complications such as strictures, leaks, or fistulas can occur after Sleeve Gastrectomy. These issues may necessitate additional surgical intervention, and in some cases, converting to a Gastric Bypass may be the most effective solution.
Understanding Gastric Bypass Surgery
Overview of Gastric Bypass
Gastric Bypass, specifically the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, is a more complex bariatric surgery that involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine. The procedure restricts food intake by reducing the stomach’s capacity and alters the digestive process to limit the absorption of calories and nutrients.
How Gastric Bypass Works
During Gastric Bypass surgery, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch from the upper portion of the stomach, roughly the size of an egg. The small intestine is then divided, and a portion of it is connected to the new stomach pouch.
This allows food to bypass the majority of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum), leading to reduced calorie and nutrient absorption.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass After Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Enhanced Weight Loss: Gastric Bypass often leads to greater weight loss compared to Sleeve Gastrectomy alone. The combination of restricted food intake and reduced nutrient absorption can help patients achieve their weight loss goals more effectively.
- Resolution of GERD: Gastric Bypass is considered one of the most effective surgical treatments for GERD, which can be a significant issue after Sleeve Gastrectomy.
- Improved Metabolic Outcomes: The hormonal changes induced by Gastric Bypass can lead to better control of type 2 diabetes, improved blood pressure, and better overall metabolic health.
The Gastric Bypass Procedure After Sleeve Gastrectomy
Preoperative Evaluation and Considerations
Before undergoing Gastric Bypass as a revisional procedure, patients must undergo a thorough preoperative evaluation.
This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests to assess the patient’s overall health and suitability for surgery.
Key Preoperative Assessments:
- Nutritional Evaluation: A comprehensive nutritional assessment is essential to identify any existing deficiencies and to plan for postoperative nutritional support.
- Psychological Evaluation: Bariatric surgery can have significant psychological impacts, and a psychological evaluation helps ensure that the patient is mentally prepared for the procedure and the lifestyle changes that follow.
- Medical Assessment: A thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging studies, and cardiovascular assessments, is necessary to identify any potential risks or contraindications.
Surgical Technique
Gastric Bypass after Sleeve Gastrectomy is a more complex procedure than a primary Gastric Bypass, as it involves revising the existing gastric anatomy. The surgery is typically performed laparoscopically, which involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments to carry out the procedure.
Steps Involved in the Procedure:
- Creation of the Stomach Pouch: The surgeon creates a small stomach pouch from the upper part of the existing sleeve gastrectomy remnant. This new pouch will serve as the primary stomach, limiting food intake.
- Rerouting the Small Intestine: The small intestine is divided, and one end is connected to the newly created stomach pouch. The other end is reattached to the small intestine further down, creating a “Y” shape.
- Reconnection and Anastomosis: The rerouted small intestine is connected to the stomach pouch and the remaining small intestine to allow food to bypass the majority of the stomach and the duodenum.
- Closure and Recovery: After completing the anastomosis, the surgeon closes the incisions, and the patient is moved to recovery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Recovery after Gastric Bypass surgery requires careful postoperative care and adherence to dietary and lifestyle guidelines. Patients will typically spend a few days in the hospital for monitoring and to manage any immediate complications.
Key Postoperative Considerations:

- Dietary Guidelines: Patients must follow a strict postoperative diet, starting with clear liquids and gradually progressing to pureed foods, soft foods, and eventually solid foods. This helps the stomach and digestive system adjust to the changes.
- Nutritional Supplements: Due to the altered digestive process, patients will need to take lifelong nutritional supplements, including vitamins and minerals, to prevent deficiencies.
- Regular Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon and dietitian are essential to monitor weight loss, nutritional status, and overall health.
Potential Complications and How to Minimize Risk
As with any surgical procedure, Gastric Bypass carries potential risks and complications. These may include:
- Dumping Syndrome: Rapid gastric emptying, or “dumping syndrome,” can occur when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: The altered digestive process can result in deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate. Lifelong supplementation and regular monitoring are necessary.
- Anastomotic Leaks: There is a risk of leaks at the surgical connections (anastomosis) between the stomach pouch and the small intestine, which can lead to infection or other serious complications.
- Bowel Obstruction: Scar tissue or hernias can cause bowel obstructions, which may require additional surgery.
Long-Term Outcomes and Weight Management
Weight Loss Expectations
Gastric Bypass after Sleeve Gastrectomy can lead to significant and sustained weight loss. On average, patients can expect to lose between 60% to 80% of their excess body weight within the first 18 to 24 months after surgery.
However, individual results may vary based on factors such as adherence to dietary guidelines, physical activity, and overall health.
Maintenance of Weight Loss
Maintaining weight loss after Gastric Bypass requires a lifelong commitment to healthy lifestyle habits, including:
- Balanced Diet: A balanced diet rich in protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is essential for maintaining weight loss and preventing nutritional deficiencies. Patients should avoid high-calorie, high-sugar, and high-fat foods that can contribute to weight regain.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a critical component of long-term weight management. Patients should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, including a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
- Behavioral Changes: Developing healthy eating habits, managing stress, and addressing emotional eating are important behavioral changes that can support long-term weight loss success.
Impact on Comorbidities and Overall Health
Gastric Bypass surgery is highly effective in improving or resolving obesity-related comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and hyperlipidemia. Many patients experience significant improvements in their overall health and quality of life following surgery.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Monitoring
Lifelong follow-up care is essential for patients who undergo Gastric Bypass after Sleeve Gastrectomy. Regular visits with the bariatric surgeon, dietitian, and primary care provider help ensure that the patient maintains optimal health, prevents complications, and addresses any nutritional deficiencies.
Psychological and Social Considerations
Mental Health Support
The psychological impact of bariatric surgery should not be underestimated. Patients may experience a range of emotions, from excitement about their weight loss to challenges related to body image and lifestyle changes.
Access to mental health support, including counseling and support groups, can be beneficial for addressing these issues and promoting long-term success.
Social Support and Lifestyle Integration
Social support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial for patients undergoing Gastric Bypass. Engaging in a supportive community, whether online or in-person, can help patients navigate the challenges of postoperative life, share experiences, and celebrate successes.
Addressing Body Image and Self-Esteem
While significant weight loss can improve body image and self-esteem, some patients may struggle with loose skin or changes in body composition. Addressing these concerns through non-surgical treatments, plastic surgery, or counseling can help patients feel more confident and satisfied with their results.
Conclusion: Achieving Long-Term Success After Gastric Bypass
Gastric Bypass after Sleeve Gastrectomy is a powerful tool for achieving significant weight loss and improving overall health.
For patients who have not achieved their desired outcomes with Sleeve Gastrectomy alone, Gastric Bypass offers a second chance to achieve their weight loss goals and resolve obesity-related comorbidities.
The long-term success of Gastric Bypass depends on the patient’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and consistent follow-up care.
By understanding the procedure, managing expectations, and seeking support when needed, patients can enjoy lasting improvements in their health, well-being, and quality of life.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
Read Also:


