The Duodenal Switch SADI-S (Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy) is an advanced and highly effective bariatric surgery that has revolutionized the field of metabolic and bariatric surgery.
As obesity rates continue to rise globally, the demand for effective weight loss surgeries has also increased. Morbid obesity, characterized by an exceedingly high Body Mass Index (BMI) and severe metabolic syndrome, necessitates advanced surgical interventions like the SADI-S procedure.
Istanbul’s Zoom Clinic, with over five years of experience in the beauty and healthcare world, stands out as a leader in providing state-of-the-art bariatric procedures, including the SADI-S.
This comprehensive guide will explore the SADI-S procedure, its benefits, risks, and long-term outcomes, offering a detailed resource for those considering this life-changing surgery.
Table of content
What is Duodenal Switch SADI-S?
The Duodenal Switch SADI-S is a modification of the traditional duodenal switch surgery, designed to provide significant weight loss while minimizing the risks associated with more complex bariatric procedures.
The SADI-S combines two key components: a gastric sleeve, which reduces the size of the stomach, and a single anastomosis that connects the duodenum directly to a loop of the small intestine, bypassing a large portion of the digestive tract.
This surgical approach limits food intake and decreases nutrient absorption, leading to substantial and sustained weight loss.

How SADI-S Differs from Traditional Duodenal Switch
The traditional duodenal switch involves two anastomoses: one between the stomach and the small intestine and another further along the small intestine.
The SADI-S, however, simplifies this process by requiring only one anastomosis, reducing the complexity of the surgery and the associated risks.
This single anastomosis makes the SADI-S a more streamlined procedure, offering similar benefits to the traditional duodenal switch but with fewer complications.
Mechanism and Benefits of SADI-S
Weight Loss Mechanism
SADI-S promotes weight loss through both restrictive and malabsorptive mechanisms. The sleeve gastrectomy portion of the surgery creates a smaller, tube-shaped stomach, which restricts the amount of food that can be consumed at one time.
This reduction in stomach size not only limits food intake but also decreases the production of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, leading to reduced appetite and less frequent feelings of hunger.
The single anastomosis connects the remaining stomach directly to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the small bowel.
This reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients, which contributes to significant excess weight loss. Patients undergoing SADI-S typically experience substantial and sustained weight loss, making it one of the most effective bariatric procedures available.
Metabolic Improvement
In addition to its weight loss benefits, SADI-S is highly effective in improving metabolic health. By altering the digestive process, SADI-S helps to resolve or improve conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea.
The procedure has shown rapid and lasting improvements in these metabolic disorders, offering patients a better quality of life and reduced risks of obesity-related diseases.
Advantages Over Other Bariatric Procedures

SADI-S offers several key advantages over other bariatric procedures:
- Greater Excess Weight Loss: Patients typically achieve greater excess weight loss with SADI-S compared to other bariatric surgeries like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.
- Simplified Surgical Process: The single anastomosis reduces the complexity of the surgery, leading to shorter operative times and lower complication rates.
- Long-Term Success: SADI-S has demonstrated long-term success in maintaining weight loss and improving metabolic health, with many patients sustaining their weight loss for years after the surgery.
- Reduced Nutritional Deficiencies: While SADI-S does reduce nutrient absorption, it generally results in fewer nutritional deficiencies compared to more complex procedures like the traditional duodenal switch.
Who Should Consider SADI-S?
Ideal Candidates
SADI-S is typically recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 or higher who have obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
It is also an excellent option for patients who have not achieved significant weight loss with other bariatric procedures, such as gastric sleeve surgery or sleeve gastrectomy.
Special Considerations
Patients with severe obesity who require significant weight loss and those with metabolic disorders that are difficult to control with other methods may particularly benefit from SADI-S.
However, due to the procedure’s complexity and potential for nutritional deficiencies, it is essential that candidates are carefully selected and thoroughly evaluated by an experienced bariatric surgeon.
The SADI-S Procedure: Step-by-Step
Preoperative Preparation
Before undergoing SADI-S, patients must undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine their suitability for the procedure.
This includes a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and a series of tests to assess the patient’s overall health and readiness for surgery. Patients are also required to follow a preoperative diet to reduce liver size and improve surgical outcomes.
Surgical Technique
- Anesthesia and Incisions: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen to allow the insertion of laparoscopic instruments.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: The first step of the surgery involves performing a sleeve gastrectomy. The surgeon removes approximately 80% of the stomach, creating a smaller, tube-shaped stomach (sleeve). This step restricts the stomach’s capacity, limiting food intake.
- Single Anastomosis: The surgeon then connects the remaining stomach to a loop of the small intestine, approximately 250 cm from the duodeno-ileal junction. This single anastomosis bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine, reducing calorie and nutrient absorption.
- Closure: Once the anastomosis is complete, the surgeon inspects the connections to ensure there are no leaks. The incisions are then closed, and the patient is moved to recovery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After surgery, patients are closely monitored in the hospital for a few days. Pain management, fluid intake, and gradual reintroduction of food are key components of the recovery process.
Patients typically start with a liquid diet, progressing to pureed foods, and eventually to solid foods over several weeks.
Potential Risks and Complications
Short-Term Risks
As with any surgery, SADI-S carries risks, including bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. However, the laparoscopic approach and the single anastomosis technique help to minimize these risks.
Long-Term Risks
Long-term complications can include nutritional deficiencies, severe malnutrition, and bile reflux. Patients may also experience dumping syndrome, where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness.
Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor for these complications and ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Nutritional Management After SADI-S
Diet and Supplementation
Due to the reduced stomach size and altered digestive process, patients must follow a specific diet and take vitamin and mineral supplements for life. Protein intake is particularly important, and patients are often advised to consume protein shakes to meet their daily requirements.
A typical diet after SADI-S includes small, frequent meals with a focus on high-protein foods, while avoiding foods high in sugar and fat. Patients must also stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor weight loss, nutritional status, and overall health. Blood tests are performed periodically to check for vitamin and mineral deficiencies, and adjustments to the diet and supplementation may be made based on these results.
SADI-S vs. Other Bariatric Procedures
SADI-S vs. Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is another popular bariatric procedure. While both SADI-S and gastric bypass involve creating a smaller stomach and bypassing part of the small intestine, SADI-S typically results in greater excess weight loss and better metabolic improvement. However, gastric bypass may be preferred for patients with a history of severe acid reflux, as SADI-S can exacerbate bile reflux in some patients.
SADI-S vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy alone involves removing a large portion of the stomach, similar to the first step of the SADI-S procedure. While sleeve gastrectomy is effective for weight loss, SADI-S offers additional benefits by including the intestinal bypass, leading to greater and more sustained weight loss, as well as better resolution of metabolic conditions.
SADI-S vs. Traditional Duodenal Switch
The traditional duodenal switch is a more complex procedure that involves two anastomoses. While it can lead to significant weight loss and metabolic improvement, it also carries a higher risk of complications and nutritional deficiencies compared to SADI-S.
The single anastomosis in SADI-S simplifies the procedure and reduces these risks, making it a preferable option for many patients.
Long-Term Outcomes of SADI-S
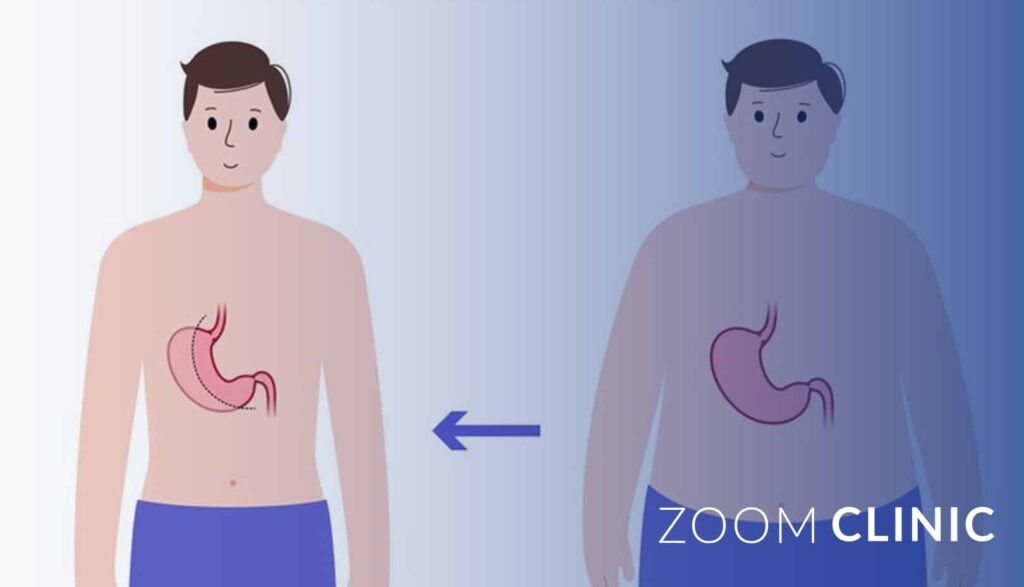
Weight Loss Success
SADI-S has been shown to result in substantial and sustained weight loss, with many patients achieving and maintaining a significant reduction in excess weight.
Studies have demonstrated that SADI-S patients typically lose more weight than those undergoing other bariatric procedures, with many patients maintaining this weight loss long-term.
Metabolic Health Improvements
In addition to weight loss, SADI-S is highly effective in improving metabolic health. Many patients experience complete remission of type 2 diabetes, and significant improvements in high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea. These improvements contribute to a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and overall better quality of life.
Quality of Life
The long-term success of SADI-S extends beyond weight loss and metabolic improvement. Many patients report a significant improvement in their quality of life, including increased energy levels, improved mobility, and enhanced self-esteem.
However, patients must be committed to lifelong dietary changes and regular follow-up care to maintain these benefits.
Challenges and Considerations
Nutritional Deficiencies
While SADI-S is associated with fewer nutritional deficiencies compared to traditional duodenal switch, patients must still be vigilant about their nutrient intake.
Lifelong supplementation of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and vitamin D, is essential to prevent severe malnutrition and related complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Successful outcomes with SADI-S require significant lifestyle changes. Patients must adhere to a strict diet, engage in regular physical activity, and attend follow-up visits with their healthcare provider. These changes are crucial to achieving and maintaining long-term success after surgery.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
The success of the SADI-S procedure also depends on the skill and experience of the bariatric surgeon. Patients considering SADI-S should seek out a high bariatric volume center, such as Zoom Clinic in Istanbul, where surgeons have extensive experience and a track record of successful outcomes.
Professor Kockman Ozturk: A Pioneer in Duodenal Switch SADI-S Surgery
In the realm of bariatric surgery, Professor Kockman Ozturk is recognized as one of the world’s foremost experts in performing the Duodenal Switch SADI-S. With years of extensive experience, Professor Ozturk has conducted over 10,000 duodenal switch surgeries, making him a pioneer in this field. His expertise ensures that patients not only achieve significant weight loss but also maintain their results long-term, with obesity not returning after surgery.
Professor Ozturk’s reputation as a leading bariatric surgeon is not only due to his surgical skills but also his commitment to patient care and education. He has trained numerous surgeons in the latest techniques and continues to contribute to advancements in bariatric surgery. For those considering SADI-S, Professor Ozturk offers the assurance of top-tier care and a successful path to a healthier life.
Conclusion
Duodenal Switch SADI-S is a highly effective bariatric procedure that offers significant weight loss and metabolic health benefits. As a streamlined variation of the traditional duodenal switch, SADI-S provides many of the same advantages with fewer risks and complications. For patients struggling with severe obesity and related metabolic disorders, SADI-S represents a promising option for long-term success.
However, the decision to undergo SADI-S should not be taken lightly. It requires a lifelong commitment to dietary changes, supplementation, and regular follow-up care. By choosing an experienced bariatric surgeon and adhering to postoperative guidelines, patients can achieve significant improvements in their health and quality of life.
Zoom Clinic in Istanbul, with its expertise in bariatric surgery and commitment to patient care, is an excellent choice for those considering SADI-S. With a comprehensive approach to patient evaluation, surgery, and follow-up care, Zoom Clinic ensures that patients receive the best possible outcomes from their weight loss surgery journey.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
Read Also:


