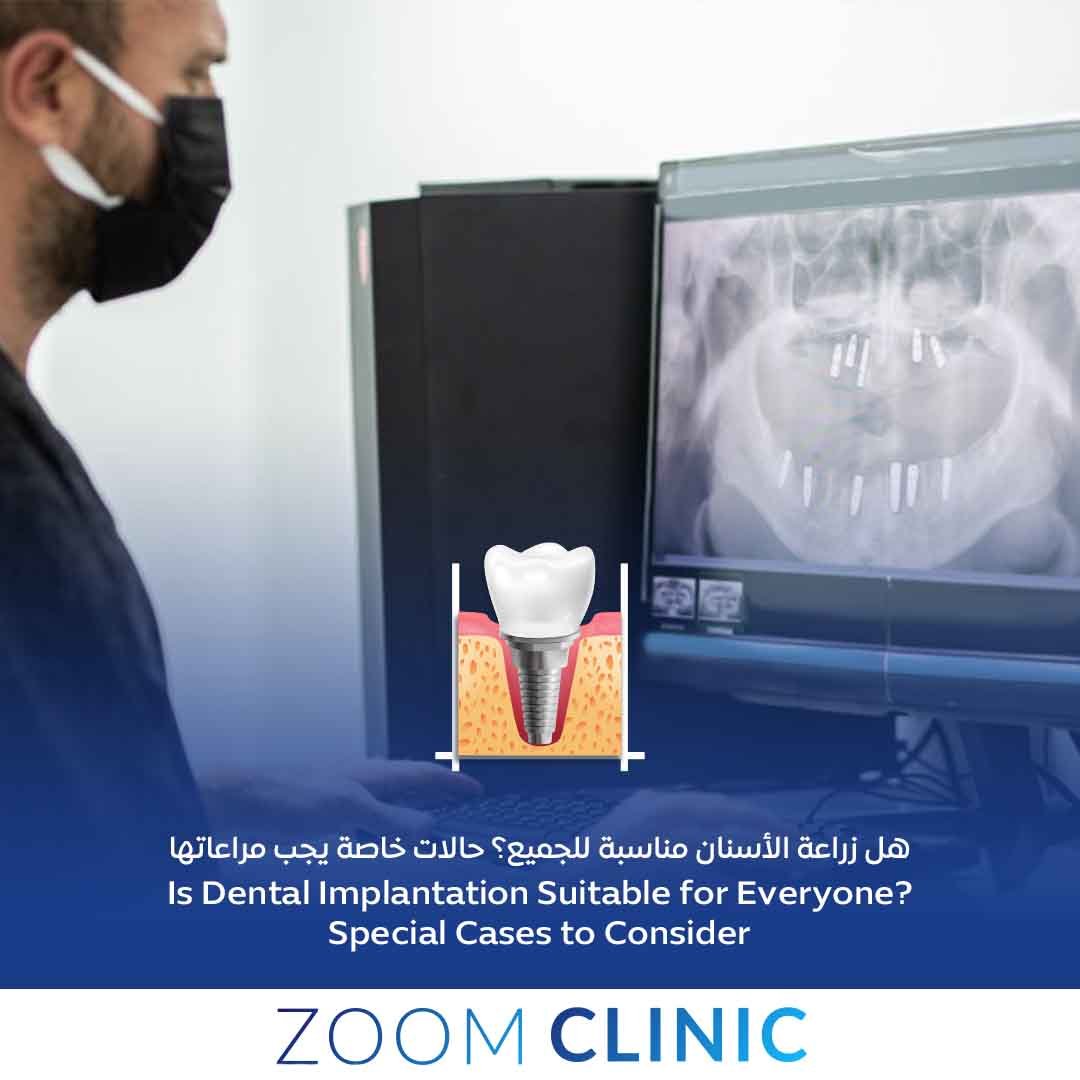
Dental implants are a popular and effective solution for missing teeth, providing stability, durability, and a natural look. However, certain health conditions can influence the success of dental implant procedures, especially in conditions like osteoporosis, sinus issues, pregnancy, and diabetes. Understanding how these factors affect dental implants can help individuals make informed decisions about their oral health and dental implant options. In this article, we’ll explore these conditions in detail Are dental implants suitable for everyone? Covering important considerations and precautions for a successful dental implant journey.
Table of content
Section 1: Dental Implants and Osteoporosis
How Osteoporosis Impacts Dental Implants
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by reduced bone density, which can lead to weaker bones. Since dental implants require a stable jawbone to anchor the implant securely, osteoporosis can sometimes be a concern for patients considering this procedure. Reduced bone density may affect the osseointegration process, where the implant fuses with the jawbone, which is essential for implant stability.
Considerations for Dental Implant Success in Osteoporosis Patients
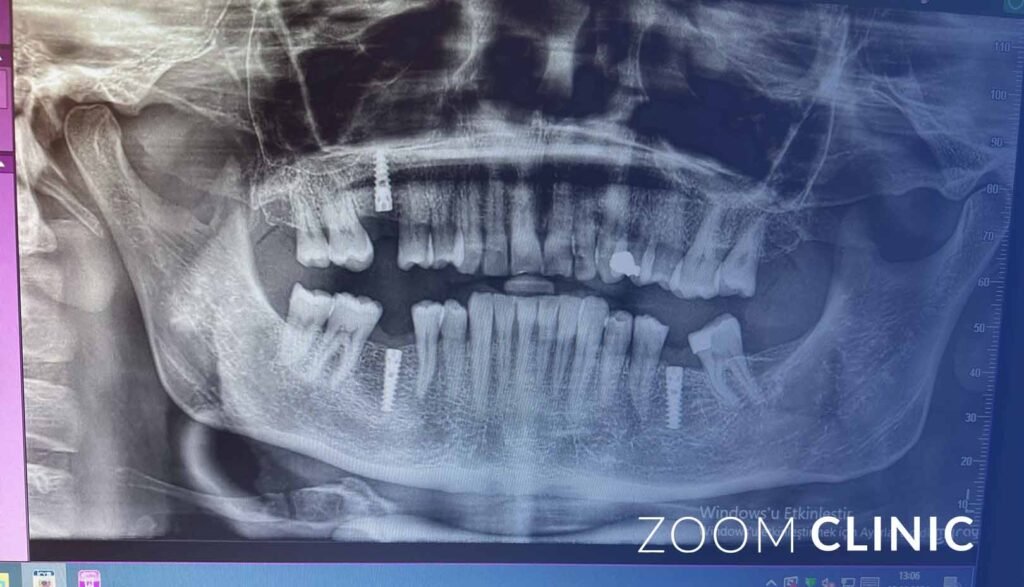
Although osteoporosis can pose challenges, patients with this condition can still successfully receive dental implants. Some key considerations include:
- Bone Density Assessment: Before the procedure, the dentist may evaluate the patient’s jawbone density using imaging technology to assess the suitability of implants.
- Bone Grafting: In cases where the jawbone lacks sufficient density, a bone graft may be recommended. This procedure helps to build up the bone, creating a solid foundation for the implant.
- Medication Awareness: Certain osteoporosis medications, particularly bisphosphonates, may impact the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Dentists will often coordinate with the patient’s doctor to determine the best approach.
Section 2: Dental Implants and Sinuses
Understanding the Connection Between Dental Implants and Sinuses
For patients receiving dental implants in the upper jaw, the proximity of the sinuses to the jawbone can sometimes be a factor. The sinuses are air-filled spaces located near the upper teeth, and in some cases, dental implants may interfere with the sinus cavity, leading to complications or discomfort.
Sinus Lift Procedure for Successful Dental Implants
To overcome this, a sinus lift procedure can be performed to create enough space and support for the implant:
- Sinus Lift: This involves lifting the sinus membrane and adding bone graft material to the area. By increasing the available bone height in the upper jaw, this procedure enables the placement of implants without affecting the sinus cavity.
- Healing Time: After a sinus lift, some healing time is required before placing the implant to ensure that the bone is strong and stable.
- Pre-Procedure Evaluation: A CT scan or X-ray is often used to assess the anatomy of the sinus and determine the need for a sinus lift.
Ideal Candidates for a Sinus Lift
While a sinus lift is a safe and effective procedure, it may not be necessary for all patients. This procedure is most commonly recommended for individuals with:
- Severe bone loss in the upper jaw
- Sinuses that are naturally close to the jawbone
- Need for implants in the upper molar or premolar area
Section 3: Dental Implants and Pregnancy
Is It Safe to Get Dental Implants During Pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a period of many physical and hormonal changes, and while oral health is crucial, major dental procedures like dental implants are generally not recommended during pregnancy. Here’s why:
- Radiation Exposure: Dental implant procedures typically involve X-rays or CT scans to evaluate bone structure, which may pose a risk to the developing fetus.
- Anesthesia Concerns: Implant surgery requires anesthesia, which may carry some risks during pregnancy.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to increased gum sensitivity and inflammation, which may affect healing and increase the risk of infection.
Recommendations for Pregnant Women Considering Dental Implants

For pregnant women, the best approach is often to wait until after pregnancy to undergo dental implant surgery. However, maintaining good oral health during pregnancy is crucial. Here are a few recommendations:
- Schedule Preventive Care: Regular cleanings and check-ups can help prevent gum disease, which is linked to pregnancy complications.
- Manage Pain and Discomfort: If a woman experiences tooth loss during pregnancy, temporary solutions, like a removable partial denture, can be considered.
- Postpartum Planning: Discussing implant options and planning the procedure for after delivery can help ensure a safe and successful implant experience.
Section 4: Dental Implants and Diabetes
The Impact of Diabetes on Dental Implant Success
Diabetes, particularly uncontrolled diabetes, can impact the success rate of dental implants. High blood sugar levels can impair blood flow and slow down the healing process, which is essential for implant stability and osseointegration. However, many diabetic patients can still be good candidates for dental implants, especially if they manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Tips for Diabetic Patients Considering Dental Implants
Here are some strategies to increase the likelihood of a successful implant procedure for diabetic patients:
- Stabilize Blood Sugar Levels: Prior to implant surgery, patients with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage blood sugar levels. Controlled diabetes significantly improves the chances of successful healing.
- Monitor Oral Health: Diabetic patients are at a higher risk of developing gum disease, which can affect the implant site. Regular dental cleanings and exams can help prevent complications.
- Communicate with Your Dentist: It’s essential for diabetic patients to inform their dentist about their condition and current medications. The dentist can work with the patient’s healthcare team to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Potential Risks and Precautions for Diabetic Patients
- Higher Risk of Infection: Due to a compromised immune system, diabetic patients may face a higher risk of infection post-surgery. Antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce this risk.
- Extended Healing Time: Diabetic patients may experience a slower healing process, so additional monitoring may be necessary during recovery.
Section 5: Dental Implants and Gum Disease
Dental implants are a leading solution to restore missing teeth and improve patients’ quality of life. However, when talking about gum disease, the relationship between them raises many questions.
Gum disease and its effect on dental implants:
Gum diseases such as gingivitis or periodontitis lead to a deterioration in overall oral health, which may negatively affect the success of dental implants. Infected gums provide an unhealthy environment for the surrounding bone, which hinders the process of implant fusion with the bone (osseointegration).
The effect of dental implants on the gums: Although dental implants are a permanent alternative, poor oral hygiene after the procedure can lead to infections in the area surrounding the implants, which is known as “peri-implantitis”.
The effect of gum disease on dental implants:
Poor osseointegration:
Gum infections lead to the erosion of the bone supporting the teeth, which weakens the bone’s ability to support the implants.
Increased risk of implant failure:
If gum disease is not treated before dental implants, it can lead to implant failure due to instability of the abutment.
Peri-implantitis:
Peri-implantitis is one of the most common complications of gum disease.
Prevention and treatment steps
Before dental implants:
- Treatment of gum disease:
- Perform a deep cleaning of the teeth.
- Use antibiotics as needed.
- Enhance bone density:
If gum disease has caused significant bone loss, bone grafting can be performed to improve the bone base.
After dental implants:
Maintain oral hygiene:
Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft brush.
Floss to clean the areas between your teeth and implants.
Regular checkups:
Visit your dentist every 6 months to check your oral health and implants.
Avoid smoking:
Smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, which negatively affects tissue healing.
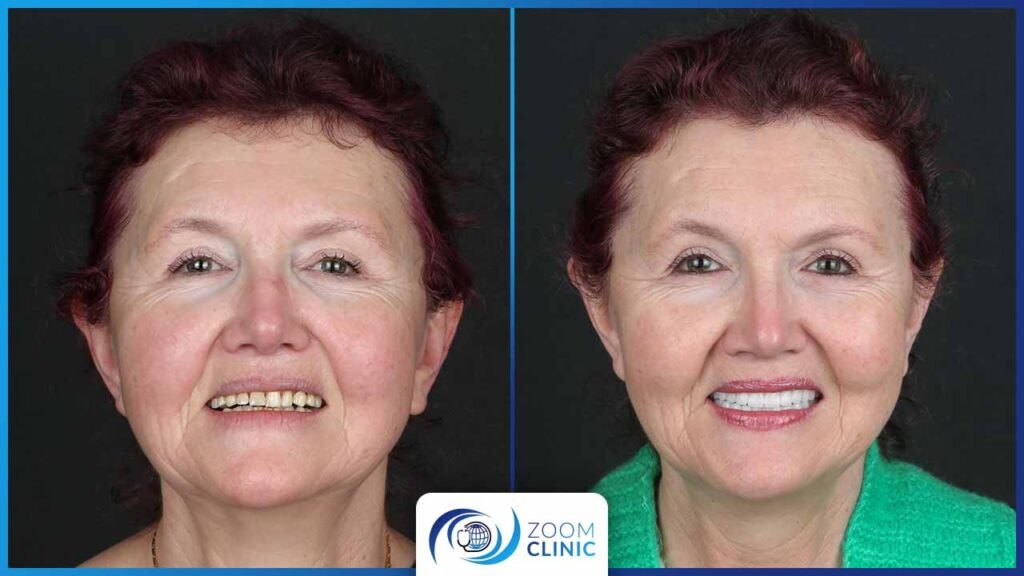
Zoom Clinic clients before and after cosmetic dentistry
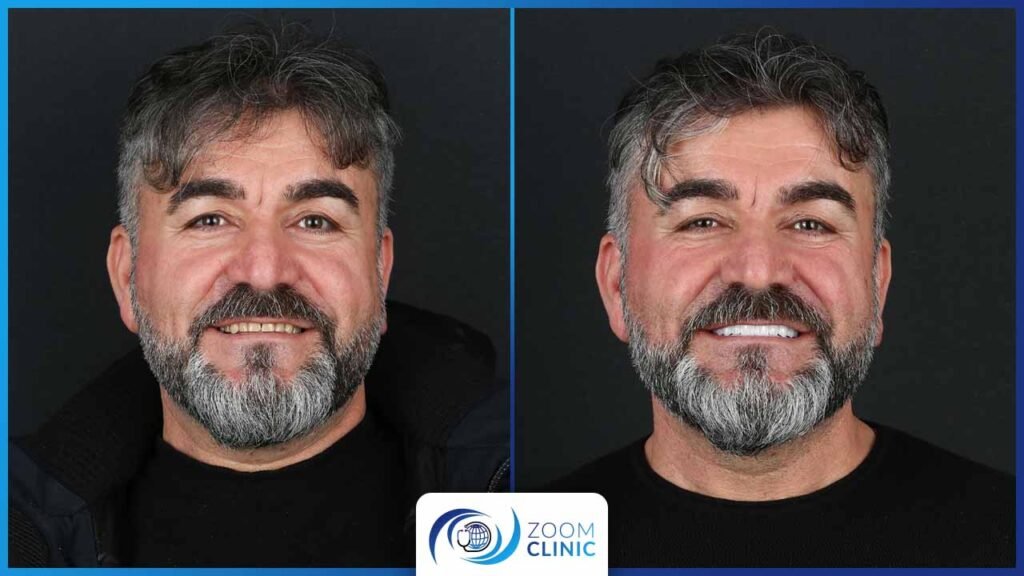
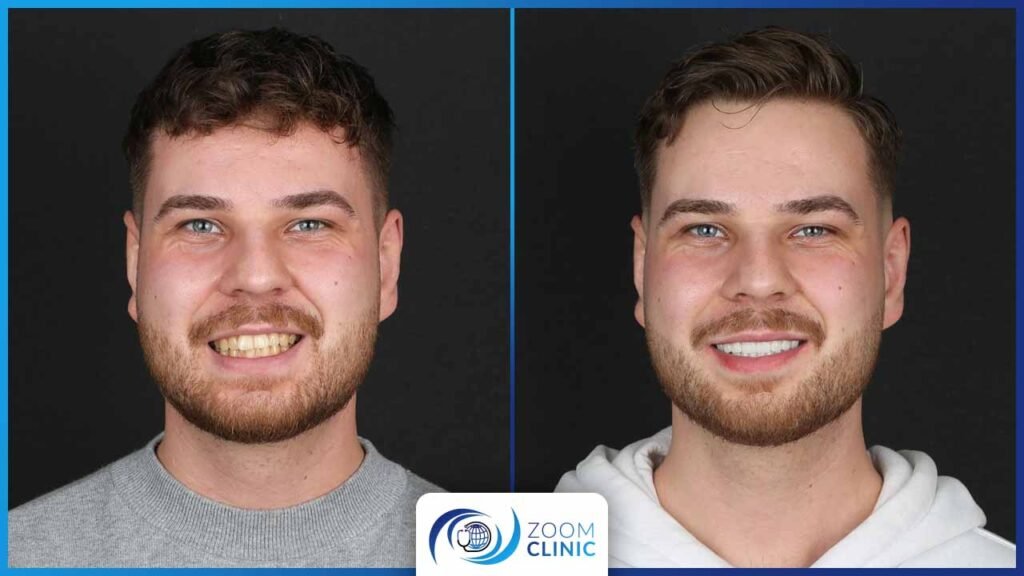
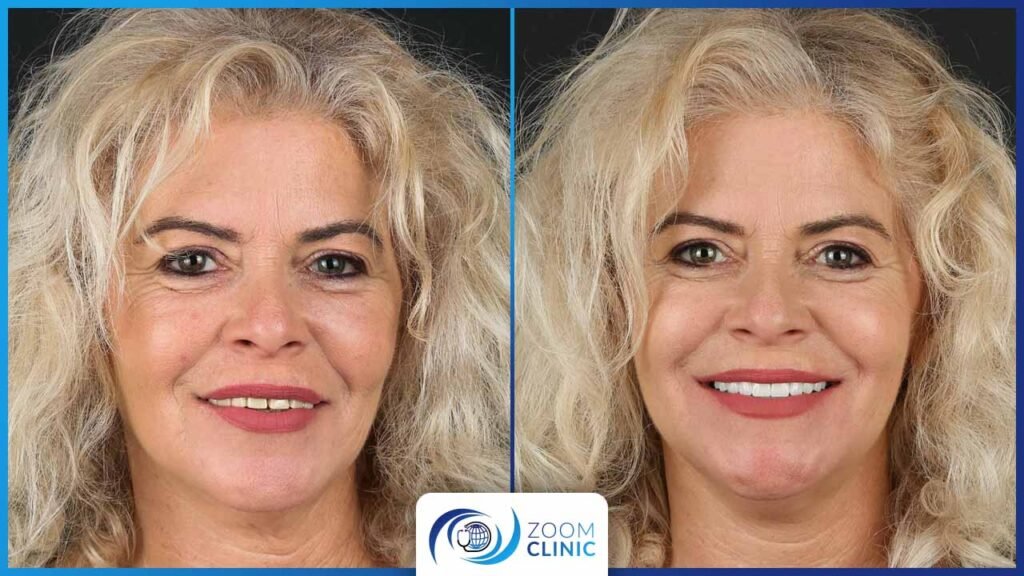
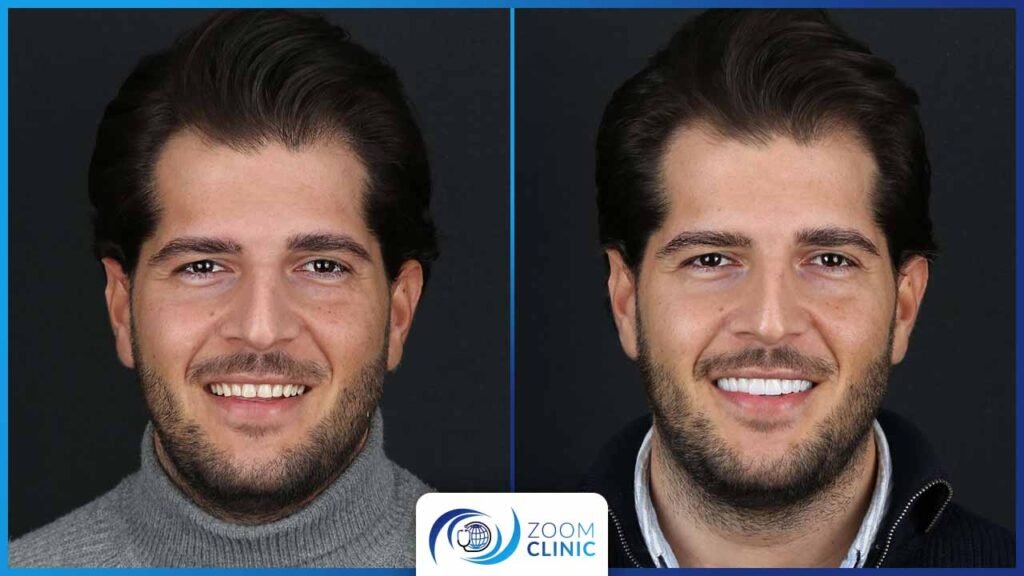




Conclusion
Dental implants offer a reliable and long-lasting solution for individuals with missing teeth, but it’s important to consider underlying health conditions that may impact the success of the procedure. Osteoporosis, sinus-related concerns, pregnancy, and diabetes each present unique challenges and considerations for patients seeking dental implants. By working closely with their healthcare and dental professionals, patients with these conditions can take proactive steps to increase the likelihood of a successful implant experience. If you have any of these conditions, be sure to consult with your dentist to explore options, discuss potential risks, and determine the best approach for achieving a healthy and confident smile.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
Related Articles: