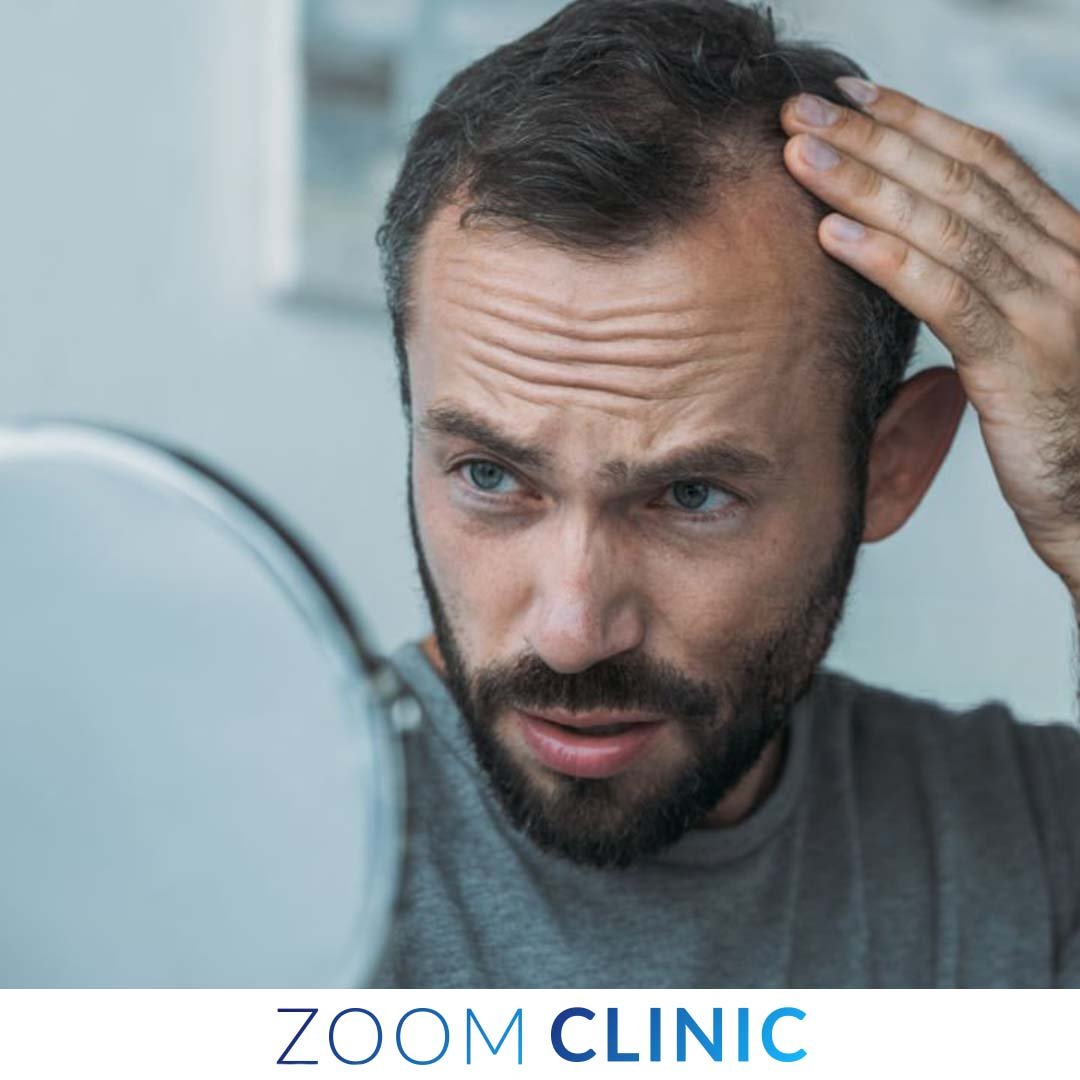
Hair loss is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. It can be distressing and significantly impact one’s self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding the causes and solutions for hair loss is crucial for those experiencing this issue. Introducing an effective hair loss treatment can help address the underlying causes and promote hair regrowth.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate various aspects of hair loss, from its causes to the most effective treatments available, including hair transplantation, which we recommend as the number one solution.
Table of content
What is Hair Loss?
Hair loss can occur for various reasons, whether temporary or permanent. The hair growth cycle involves three main phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase where hair growth slows), and telogen (resting phase). Disruptions in this cycle can lead to hair thinning and hair loss.
Types of Hair Loss: Female Pattern Hair Loss
Androgenic Alopecia: Also known as male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness, this hereditary type of hair loss affects both men and women. Men typically experience receding hairlines and thinning at the crown, while women may notice overall hair thinning and widening of the part line.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss. It can affect any body part and may progress to total hair loss (alopecia totalis).
Telogen Effluvium: This temporary type of hair loss occurs when many hair follicles enter the telogen phase simultaneously. It can be triggered by stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
Traction Alopecia is hair loss caused by prolonged tension on the hair, often caused by hairstyles like tight braids or ponytails.
Scarring Alopecia is permanent hair loss caused by conditions that cause scalp scarring, such as lichen planopilaris or frontal fibrosing alopecia.
Anagen Effluvium: Rapid hair loss due to medical treatments like chemotherapy, which target rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles.
Causes of Hair Loss
Genetics: Hereditary hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss, affecting both men and women. People with this condition often lose hair not only from the scalp but also from other areas such as eyebrows and eyelashes.
Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid problems can cause hormonal fluctuations and hair loss.
Medical Conditions: Scalp infections, skin disorders (like psoriasis), and systemic conditions (like lupus) can contribute to hair loss.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and vitamins can weaken hair follicles and lead to hair thinning and loss.
Medications: Certain drugs used for treating cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, and high blood pressure can have side effects that include hair loss.
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger telogen effluvium, leading to noticeable hair shedding.
Hair Care Practices: Overusing styling tools, chemical treatments, and harsh hair care products can damage hair follicles and contribute to hair loss.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hair loss symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common signs include:
- Gradual thinning on the top of the head
- Circular or patchy bald spots
- Sudden loosening of hair
- Full-body hair loss
- Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp
To diagnose the cause of hair loss, a healthcare provider may perform:
Physical Examination: Check the scalp and hair for hair loss patterns.
Medical History: Review the patient’s health history, including a family history of hair loss.
Blood Tests: To identify underlying medical conditions or nutrient deficiencies.
Scalp Biopsy: Taking a small sample of scalp tissue for lab analysis.
Pull Test: Gently pull several hairs to see how many come out to assess hair shedding.
Treatment Options
1. Medications
Minoxidil (Rogaine): An over-the-counter topical treatment that can stimulate hair growth and slow hair loss.
Finasteride (Propecia) is a prescription oral medication for men that reduces hair loss by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to androgenetic alopecia.
Corticosteroids: Injections or topical treatments for autoimmune hair loss like alopecia areata.
Anti-androgens: Medications like spironolactone can help reduce androgen levels in women with hair loss.
2. Non-Surgical Treatments
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This treatment involves injecting the patient’s platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to promote hair growth.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive treatment that uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair regrowth.
3. Surgical Treatments
Hair Transplantation: This procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor site (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to areas with thinning or no hair. It is highly effective and offers permanent results.
4. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Balanced Diet: Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamins.
Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh treatments and styles that stress the hair.
Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and regular exercise can help reduce stress-related hair loss.
Hair Transplantation: The Ultimate Solution
Hair transplantation is the most effective solution for permanent hair loss. The procedure has evolved significantly, offering natural-looking and long-lasting results.
Benefits of Hair Transplantation
Natural Results: Transplanted hair blends seamlessly with existing hair, providing a natural look.
Permanent Solution: Unlike temporary treatments, hair transplantation offers a long-term solution to hair loss.
Minimal Downtime: Patients can resume normal activities within a few days post-procedure.
High Success Rate: Hair transplantation boasts a high success rate, making it a reliable option for many individuals.
Considerations and Expectations
Cost: Hair transplantation can be expensive, but the permanent results often justify the investment.
Suitability: Only some people are suitable candidates for hair transplantation. Factors like the extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, and overall health must be considered.
Post-Procedure Care: Proper aftercare is essential for the transplant’s success. This includes following the surgeon’s instructions, avoiding strenuous activities, and taking prescribed medications.
Other Solutions for Hair Loss
While hair transplantation remains the gold standard for treating hair loss, several other effective solutions can complement or serve as alternatives, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Topical Treatments
Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter topical treatment is applied directly to the scalp and has been proven to stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss. It’s available in liquid and foam forms and is suitable for both men and women.
Oral Medications
Finasteride (Propecia): This prescription oral medication is particularly effective for men with androgenetic alopecia. It works by inhibiting the production of DHT, a hormone that contributes to hair loss.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
Biotin: Often marketed as a hair growth supplement, biotin (a B vitamin) supports overall hair health. While scientific evidence is mixed, many people report positive results.
Saw Palmetto: A natural supplement that may help reduce hair loss by blocking DHT production.
Essential Oils: When massaged into the scalp regularly, rosemary, peppermint, and lavender promote hair growth.
Laser Therapy
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This non-invasive treatment uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles and encourage regrowth. Devices such as laser combs, helmets, and caps are available for home use.
PRP Therapy
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: In this treatment, a patient’s blood is drawn and processed to extract plasma rich in growth factors. The PRP is injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve hair thickness.
Lifestyle Changes
Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly those that support hair health (like iron, zinc, and vitamin D), is essential. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fish can produce healthier hair.
Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. Yoga, meditation, and regular physical activity can help manage stress and promote well-being.
Hair Care Practices
Gentle Hair Handling: To prevent further damage to hair follicles, avoid harsh brushing, tight hairstyles, and excessive use of heat styling tools.
Suitable Hair Products: Use shampoos and conditioners designed for your hair type and avoid products with harsh chemicals that can damage hair.
Scalp Micropigmentation
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) is a non-surgical treatment in which natural pigments are applied to the scalp to create the appearance of fuller hair. This can be particularly effective for those with thinning hair or small bald patches.
Wigs and Hairpieces
Wigs and Hairpieces: Wigs and hairpieces offer an excellent option for those who prefer a non-invasive and immediate solution. Modern wigs are designed to look natural and can be styled just like natural hair.
Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture can stimulate hair follicles and improve hair growth. While more research is needed, it can be a complementary therapy.
Herbal Remedies: Traditional medicine is often used. Herbs like ginseng and aloe vera promote hair. While evidence varies, these remedies are generally safe and can be part of a holistic approach to hair care.
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Hair Loss
Hair loss can have profound psychological and emotional impacts on individuals. Hair’s significance in our society cannot be underestimated, as it is often associated with beauty, youth, and identity. When hair loss occurs, it can lead to a range of emotional responses and mental health challenges.
Self-Esteem and Body Image
Hair is a crucial aspect of personal identity for many people, and losing hair can significantly affect one’s self-esteem and body image. Individuals may feel less attractive and struggle with their self-worth. This can be particularly challenging for women, as societal norms often emphasize the importance of hair in defining femininity and beauty.
Social Anxiety and Isolation
Hair loss can lead to social anxiety and a reluctance to engage in social activities. People experiencing hair loss might avoid social gatherings, feel embarrassed about their appearance, and worry about being judged by others. This can result in social withdrawal and isolation, which further exacerbates feelings of loneliness and depression.
Impact on Professional Life
In the professional realm, hair loss can affect an individual’s confidence and performance. Those experiencing hair loss may feel self-conscious during meetings, presentations, or interviews, fearing that their hair loss will negatively influence others’ perceptions of their competence and professionalism.
Mental Health Issues
The emotional toll of hair loss can contribute to severe mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and even body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). Individuals may become preoccupied with their hair loss, leading to excessive worry and distress. It’s essential for those experiencing significant emotional distress due to hair loss to seek professional help from mental health professionals.
Coping Mechanisms
Support Groups: Joining a support group with others experiencing hair loss can provide a sense of community and understanding. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can be incredibly therapeutic.
Counseling and Therapy: Speaking with a therapist can help individuals process their feelings about hair loss and develop healthy coping mechanisms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can effectively address negative thought patterns.
Open Communication: Discussing hair loss with family and friends can alleviate some of the emotional burden and foster understanding and support from loved ones.
Adopting New Hairstyles: Experimenting with different hairstyles, wigs, or hairpieces can help individuals feel more comfortable and confident in their appearance. Modern wigs and hairpieces are designed to look natural and can be a practical solution for those struggling with hair loss.
Focusing on Overall Well-being: Engaging in activities that promote physical and mental well-being, such as regular exercise, meditation, and hobbies, can improve mood and reduce stress related to hair loss.
Importance of Professional Support
Healthcare providers, including dermatologists and mental health professionals, play a crucial role in addressing the psychological impact of hair loss. They can provide medical treatments for hair loss, offer counseling, and refer patients to support groups and therapists.
Hair loss is not just a physical condition but a deeply emotional experience that can affect various aspects of an individual’s life.
Preventing Further Hair Loss
While hair transplantation provides a permanent solution, it is also essential to prevent further hair loss and maintain the health of the transplanted hair. Here are some tips:
Healthy Diet: Ensure a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support hair health.
Gentle Hair Care: Use mild shampoos and conditioners, avoid excessive heat styling, and be gentle when brushing or combing hair.
Regular Check-ups: Monitor hair health and consult a healthcare provider if you notice significant changes.
Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine.
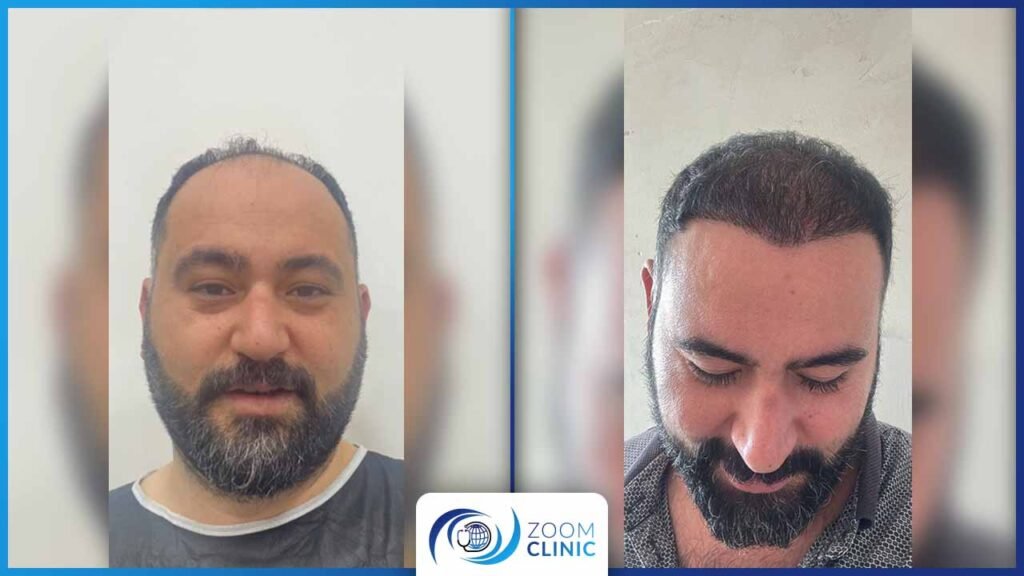
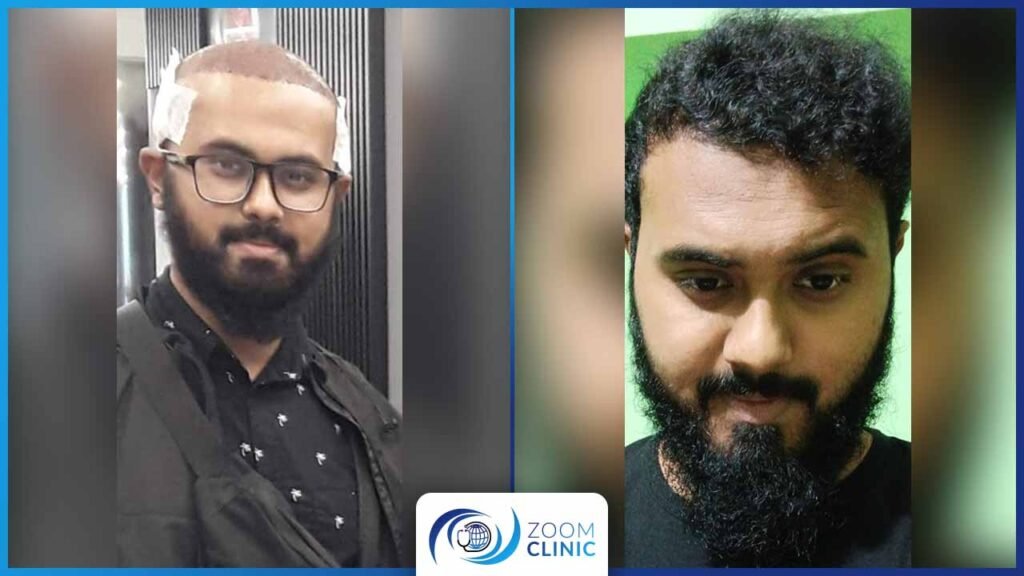
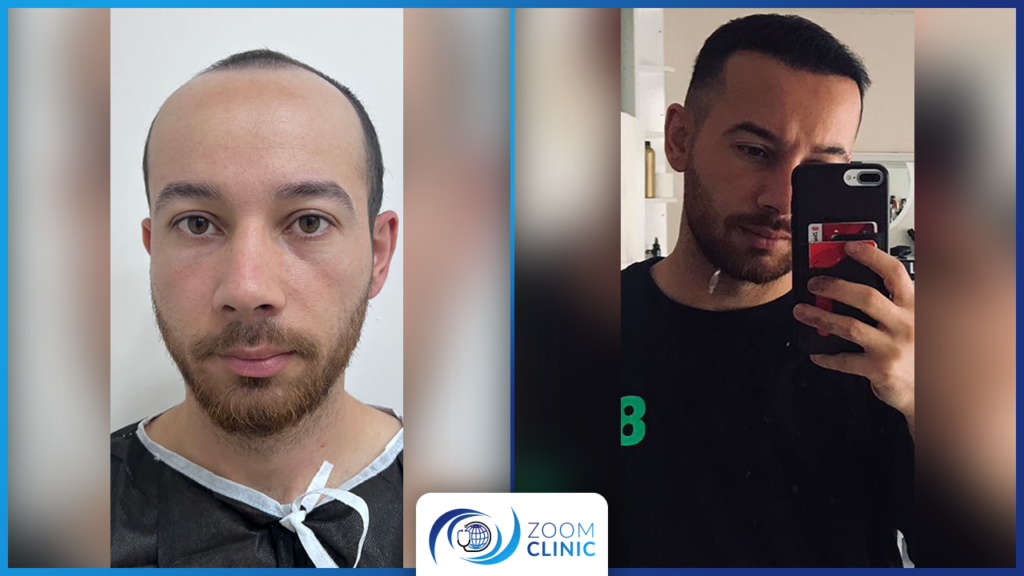
Zoom Clinic clients before and after hair transplantation
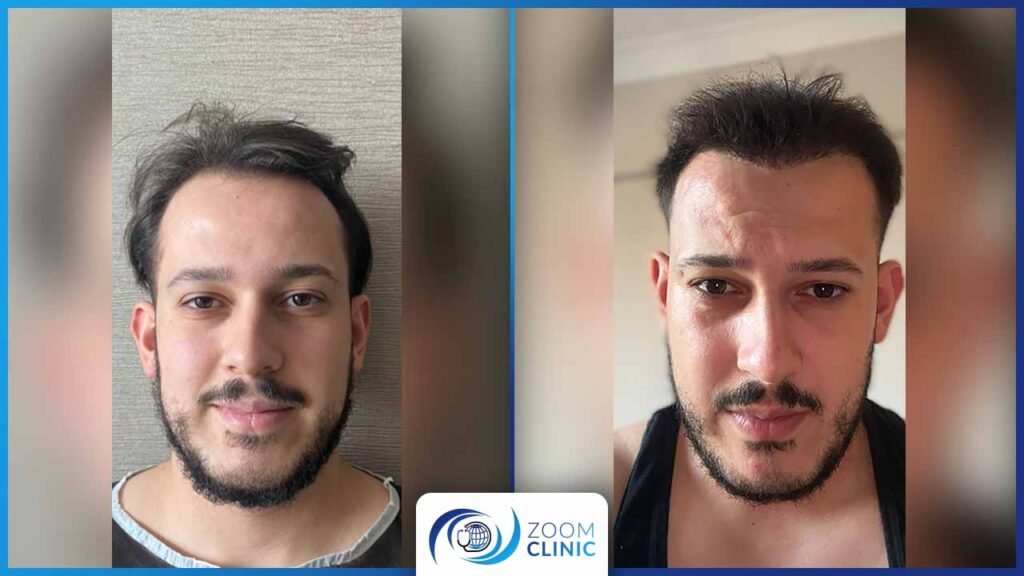
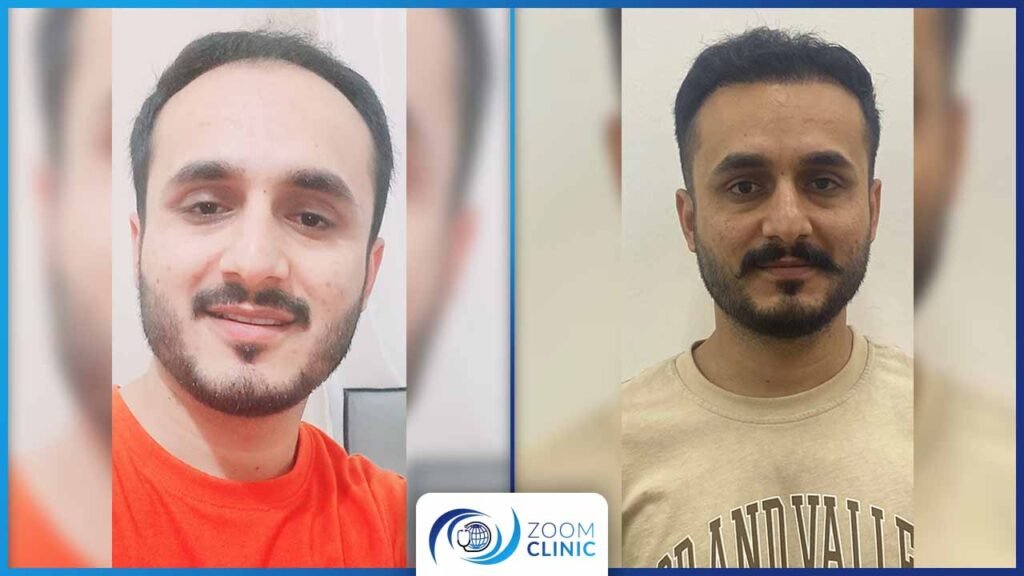




Conclusion
Hair loss can be a challenging condition to deal with, but understanding its causes and exploring effective solutions can help manage and overcome it.
While various treatments are available, hair transplantation is the most reliable and permanent solution. Individuals can achieve and maintain healthy hair growth by combining medical therapies, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures.
If you are experiencing hair loss, consult with a healthcare provider or a hair loss specialist to determine the best course of action for your situation.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic
Read Also:


