Obesity is a significant health concern globally, affecting millions of individuals across various age groups. Women of reproductive age with severe obesity face unique challenges, particularly concerning pregnancy.
Individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 40 or 35 with obesity-related conditions may qualify for bariatric surgery. Bariatric surgery, a popular weight loss intervention, has shown promise in helping individuals achieve a healthy weight.
This article explores the intricate relationship between obesity operations and pregnancy, focusing on the impact of weight loss surgery on maternal and fetal health, potential complications, and the journey toward a healthy pregnancy.
Table of Content
Understanding Bariatric Surgery
Types of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery encompasses various procedures designed to help individuals lose weight by altering the digestive system. The most common types include:
Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)
This procedure involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. As a result, food bypasses most of the stomach and part of the small intestine, leading to reduced calorie absorption.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
This procedure removes a significant portion of the stomach, leaving a banana-shaped section. This smaller stomach limits food intake and reduces hunger hormones.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
A band is placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the amount of food intake.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
This complex procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach and bypassing a significant section of the small intestine. It significantly limits food intake and nutrient absorption.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery offers numerous benefits, including:
- Significant weight loss
- Improvement or resolution of obesity-related health problems such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and joint pain
- Enhanced quality of life
- Increased fertility and improved reproductive outcomes for women
Obesity and Pregnancy: Challenges and Risks
Impact of Obesity on Pregnancy
Obesity during pregnancy poses several risks for both the mother and the baby. These include:
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM): Obese women have a higher risk of developing GDM, which can lead to complications such as macrosomia (large baby), preterm birth, and birth injuries.
- Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: These conditions involve high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can lead to severe complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Increased Risk of Cesarean Delivery: Obesity increases the likelihood of requiring a cesarean section, which carries additional risks compared to vaginal delivery.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Obese women are at risk of nutrient deficiencies, which can affect fetal development and maternal health.
- Sleep Apnea: This condition, common in obese individuals, can lead to complications such as hypoxia (low oxygen levels) and cardiovascular issues during pregnancy.
Impact on Fertility
Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances and reduced fertility in women of reproductive age. It affects ovulation and can result in conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which further complicates the ability to conceive.
Pregnancy After Bariatric Surgery
Timing of Pregnancy Post-Surgery
It is generally recommended to wait at least 12-18 months after undergoing bariatric surgery before attempting to conceive.
This waiting period allows the body to stabilize and adapt to the new metabolic state, ensuring that rapid weight loss and nutritional deficiencies are managed effectively.
Benefits of Weight Loss Surgery on Pregnancy
Reduced Risk of Gestational Diabetes and Hypertension: Weight loss post-surgery significantly lowers the risk of developing gestational diabetes and hypertension, leading to healthier pregnancy outcomes.
Improved Fertility: Many women experience restored fertility and regular menstrual cycles following significant weight loss, making it easier to conceive.
Healthier Maternal Weight Gain: Weight loss surgery helps women achieve and maintain a healthy weight, promoting appropriate maternal weight gain during pregnancy.
Special Considerations and Nutritional Care
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Post-bariatric surgery patients risk deficiencies in essential nutrients such as iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Monitoring and managing these deficiencies is crucial to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Supplementation:
Regularly taking prescribed supplements is essential to address common nutrient deficiencies and support fetal growth and development.
Diet and Meal Planning:
A balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals is vital. Pregnant women should work closely with a dietitian to create a meal plan that meets their nutritional needs without overloading their reduced stomach capacity.
Potential Surgical Complications
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort:
Post-surgery, some women may experience abdominal pain or discomfort during pregnancy. It is essential to seek medical advice if these symptoms occur.
Dumping Syndrome:
This condition, characterized by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea after eating, can affect some women post-surgery. Managing diet and meal timing can help alleviate symptoms.
Increased Risk of Small for Gestational Age (SGA) Babies:
While weight loss surgery reduces many risks, there is a potential for babies to be born smaller than average. Close monitoring of fetal growth is necessary.
Pregnancy Outcomes and Post-Operative Care
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Prenatal Visits: Regular prenatal visits are crucial for monitoring the health of both the mother and the baby. These visits should include assessments of weight gain, nutritional status, and fetal growth.
Multidisciplinary Team: A care team comprising a bariatric surgeon, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, dietitian, and obstetrician ensures comprehensive care and promptly addresses complications.
Cesarean Delivery and Recovery
Higher Risk of Cesarean Section: Women who have undergone bariatric surgery may have a higher risk of cesarean delivery due to previous abdominal surgeries and complications.
Recovery: Post-cesarean recovery should include pain management, infection monitoring, and nutritional support to facilitate healing.
Nutritional and Surgical Complications
Common Nutritional Deficiencies
Women who have undergone bariatric surgery may face several nutritional challenges during pregnancy, which can affect both maternal and fetal health. Addressing these deficiencies is crucial for a healthy pregnancy.
Iron Deficiency: Iron deficiency anemia is common in post-bariatric surgery patients due to reduced stomach capacity and altered digestion. Iron supplements and iron-rich foods prevent anemia and support fetal development.
Calcium and Vitamin D Deficiency: These nutrients are vital for bone health. Bariatric surgery can impair their absorption, leading to deficiencies that affect both the mother’s and the baby’s skeletal development. Regular supplementation and monitoring are necessary.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency: These vitamins are crucial for nerve function and preventing congenital anomalies. Deficiencies can lead to neurological issues in the mother and neural tube defects in the baby. Regular supplementation and dietary adjustments are required.
Protein Deficiency: Adequate protein intake is vital for fetal growth and maternal health. Post-surgery patients must focus on high-protein foods and possibly protein supplements to meet their increased needs.
Managing Nutritional Deficiencies
Regular Monitoring: Frequent blood tests to monitor nutrient levels and ensure deficiencies are promptly addressed.
Dietary Adjustments: Working with a dietitian to create a nutrient-dense meal plan that meets the unique needs of pregnancy after bariatric surgery.
Supplementation: Adhering to prescribed supplements to maintain optimal nutrient levels.
Surgical Complications
Internal Hernias: Bariatric surgery can increase the risk of internal hernias, which may cause abdominal pain and complications during pregnancy. Prompt medical attention is essential if symptoms occur.
Adhesions: Scar tissue from previous surgeries can lead to adhesions, which can cause pain and potentially affect the pregnancy. Regular monitoring and consultation with a bariatric surgeon are crucial.
Nutritional and Surgical Complications Management: Collaboration with a multidisciplinary team ensures that surgical and nutritional complications are managed effectively, promoting a healthy pregnancy.
Maternal and Fetal Health
Maternal Health
Healthy Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight throughout pregnancy reduces the risk of complications and supports overall well-being.
Monitoring and Support: Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures that issues are addressed promptly, promoting a healthy pregnancy.
Fetal Health
Fetal Growth Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds and assessments ensure that the baby grows appropriately and that potential issues are identified early.
Preventing Congenital Anomalies: Addressing nutritional deficiencies and maintaining a balanced diet reduces the risk of congenital anomalies and supports healthy fetal development.
Pregnancy After Different Types of Bariatric Surgery
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Nutritional Considerations: Gastric bypass surgery can lead to significant nutritional deficiencies. Regular monitoring and supplementation are essential to support a healthy pregnancy.
Risk of Dumping Syndrome: Managing diet and meal timing can help alleviate symptoms of dumping syndrome during pregnancy.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Nutritional Support: Ensuring adequate nutrient intake is crucial, as a smaller stomach capacity can limit food intake. Regular consultations with a dietitian help manage dietary needs.
Monitoring for Complications: Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures that complications are promptly addressed.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
Adjusting the Band: The gastric band may need adjustment during pregnancy to accommodate changes in dietary needs and ensure maternal and fetal health.
Monitoring Nutritional Status: Regular monitoring of nutrient levels and dietary adjustments are essential to prevent deficiencies.
Psychological and Emotional Considerations
Psychological Impact of Bariatric Surgery
Body Image and Self-Esteem: Significant weight loss can impact body image and self-esteem. Addressing these changes and seeking support when needed is crucial for mental well-being.
Mental Health Support: Access to mental health professionals and support groups can help manage the psychological impact of bariatric surgery and pregnancy.
Emotional Well-Being During Pregnancy
Managing Expectations: Understanding the changes that come with pregnancy after bariatric surgery helps manage expectations and reduce stress.
Support Systems: Building a solid support system of family, friends, and healthcare providers promotes emotional well-being during pregnancy.
The Role of the Healthcare Team
Multidisciplinary Care Team
- Bariatric Surgeon: The bariatric surgeon monitors the patient’s progress and addresses any surgical complications.
- Maternal-Fetal Medicine Specialist: This specialist oversees the pregnancy, maintaining maternal and fetal health.
- Dietitian: The dietitian helps manage nutritional needs and addresses any deficiencies.
- Obstetrician: The obstetrician provides routine prenatal care and manages the delivery process.
Collaborative Care Approach
- Regular Communication: Regular communication between team members ensures comprehensive care and promptly addresses issues.
- Patient-Centered Care: Focusing on the patient’s unique needs and preferences promotes a positive pregnancy experience.
Conclusion
Pregnancy after bariatric surgery presents unique challenges and opportunities. With careful planning, regular monitoring, and a supportive healthcare team, women undergoing weight loss surgery can achieve healthy pregnancies and positive outcomes.
Addressing nutritional deficiencies, managing surgical complications, and promoting emotional well-being are essential to a successful pregnancy.
By understanding the impact of obesity operations on pregnancy and taking proactive steps, women can navigate this journey with confidence and optimism.
Choosing bariatric surgery can be a transformative step towards achieving a healthy weight and improving overall health.
For women of reproductive age, it can also pave the way for a healthier pregnancy and a brighter future for both mother and child.
Zoom Clinic clients before and after obesity surgeries
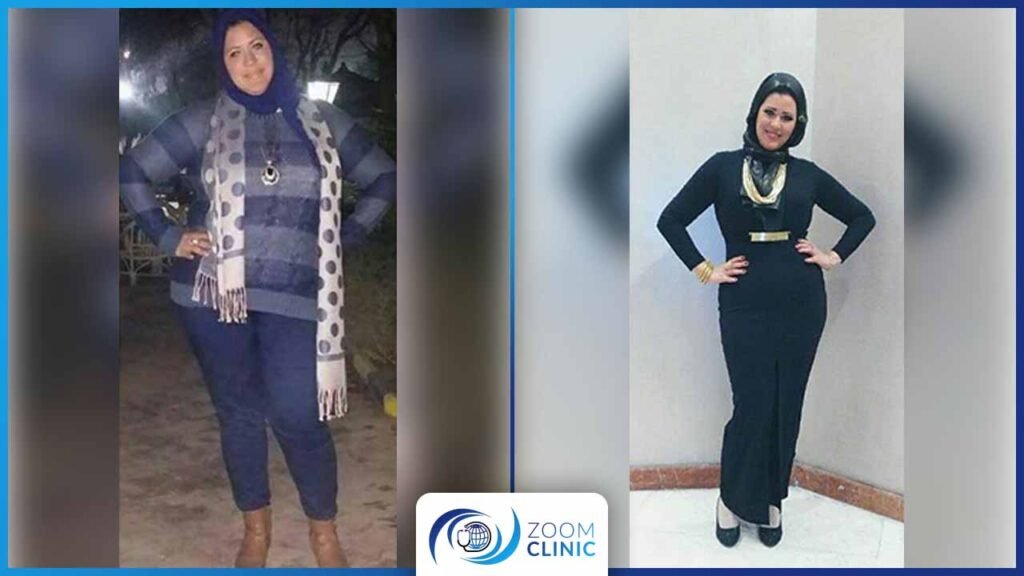
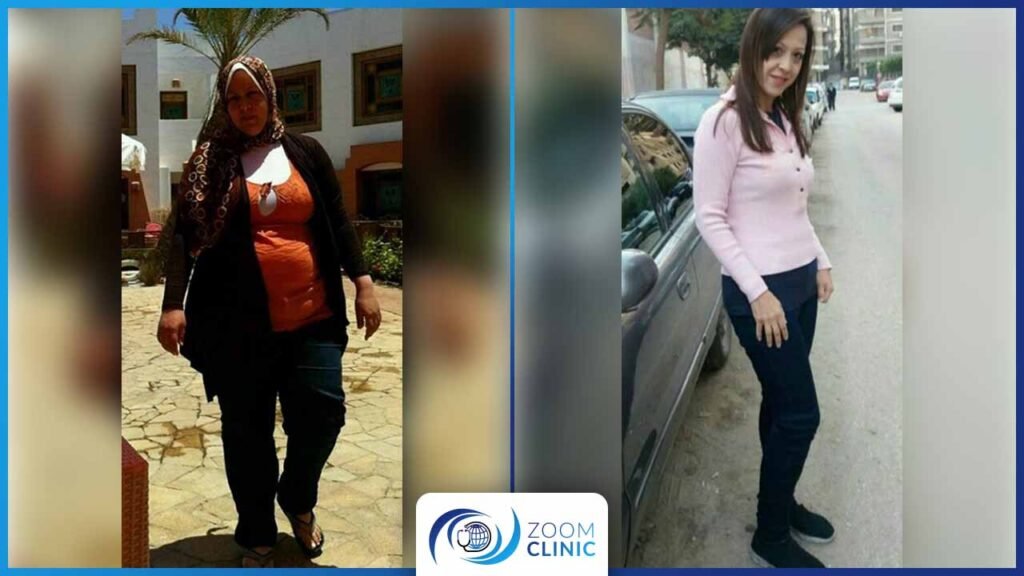
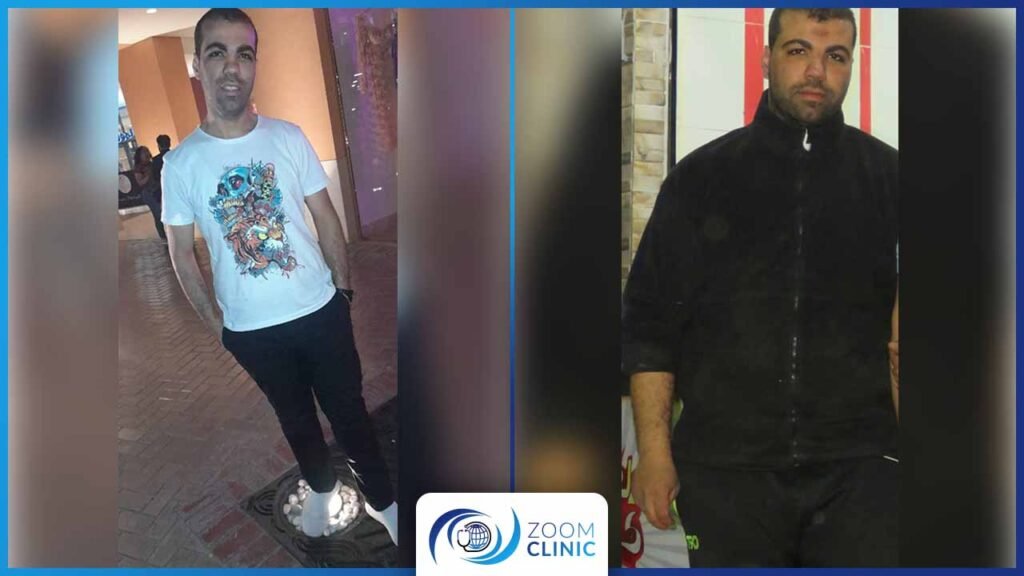
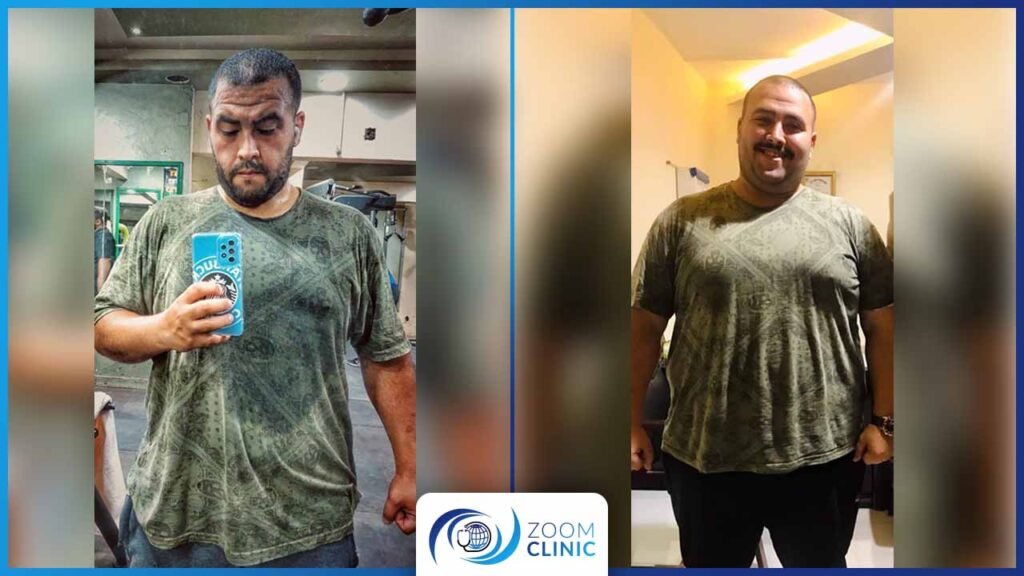
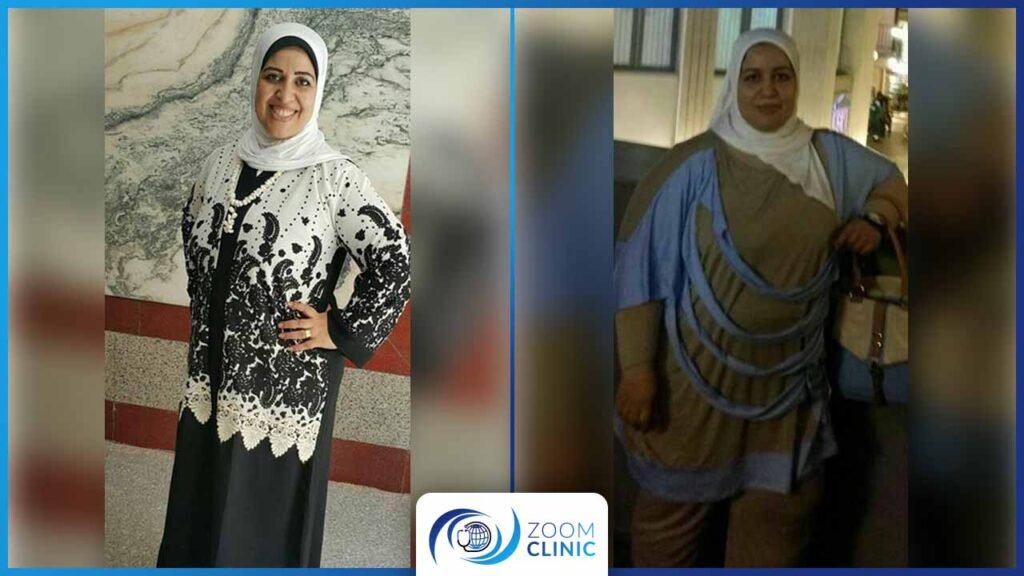
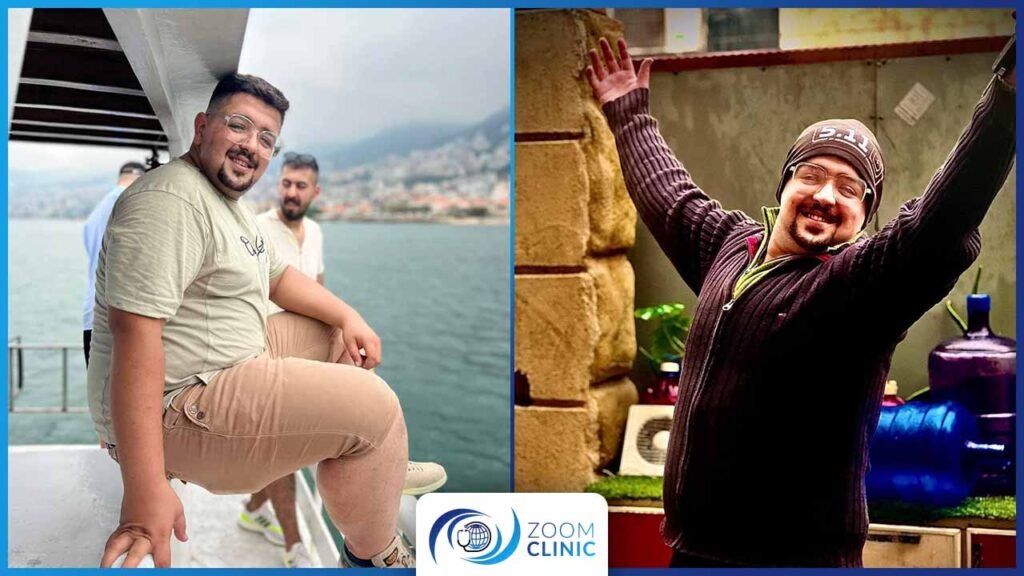







For more, Browse Our Results
Top 10 FAQs about Obesity Operations and Pregnancy
Pregnancy after bariatric surgery is a journey that requires careful planning, close monitoring, and collaboration with a multidisciplinary healthcare team.
Understanding the benefits, risks, and necessary precautions can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and positive outcomes for both mother and baby.
Women who have undergone bariatric surgery can achieve successful and healthy pregnancies by addressing nutritional needs, managing potential complications, and maintaining regular prenatal care.
1. Can I get pregnant after bariatric surgery?
Yes, you can get pregnant after bariatric surgery. It is generally recommended to wait at least 12-18 months post-surgery before attempting to conceive. This waiting period allows your body to stabilize and adapt to significant weight loss and nutritional changes, ensuring a healthier pregnancy.
2. What are the benefits of getting pregnant after losing weight from bariatric surgery?
Pregnancy after significant weight loss from bariatric surgery can reduce the risk of complications such as gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia. Achieving a healthier weight improves maternal and fetal outcomes, leading to a healthier pregnancy.
3. Are there any risks associated with pregnancy after bariatric surgery?
While pregnancy after bariatric surgery can be healthy, some risks must be aware of, including nutritional deficiencies (such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12), potential for small for gestational age (SGA) babies, and complications related to the surgery itself, such as internal hernias or adhesions. Close monitoring and a multidisciplinary care approach are essential.
4. How does bariatric surgery affect fertility?
Bariatric surgery can improve fertility, especially in women with obesity-related hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Weight loss can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve ovulation, making conceiving easier.
5. What nutritional supplements will I need during pregnancy after bariatric surgery?
After bariatric surgery, you will likely need additional supplements to address common nutrient deficiencies. These typically include iron, calcium, vitamin D, B12, and folic acid. Your healthcare provider will recommend specific supplements based on your nutritional status.
6. Will I need to follow a special diet during pregnancy after bariatricrgery?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs is crucial. Focus on nutrient-dense foods rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals. Working with a dietitian can help you create a meal plan that ensures you and your baby receive adequate nutrition.
7. Can I have a vaginal delivery after bariatric surgery, or will I need a cesarean section?
Many women can have a vaginal delivery after bariatric surgery. However, there may be a higher risk of cesarean delivery due to factors such as previous abdominal surgeries and potential complications. Your obstetrician will monitor your pregnancy and advise on the best delivery method.
8. What should I expect during prenatal care after bariatric surgery?
Prenatal care will involve regular visits to monitor your health and the baby’s development. This includes frequent blood tests to check for nutritional deficiencies, ultrasounds to track fetal growth, and consultations with a multidisciplinary care team, including a bariatric surgeon, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, and dietitian.
9. Are there any special considerations for women who have undergone different types of bariatric surgery (e.g., gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy)?
Yes, different types of bariatric surgery can have varying impacts on pregnancy. For example, gastric bypass surgery may lead to more significant nutritional deficiencies, while adjustable gastric banding might require adjustments during pregnancy. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to manage any specific risks associated with your type of surgery.
10. What are the long-term health benefits of having a pregnancy after bariatric surgery?
Long-term health benefits include maintaining a healthier weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related complications, and improving overall well-being. Successful weight and nutrition management during pregnancy can also set a positive example for maintaining a healthy lifestyle post-pregnancy.
Get the special offer today from Zoom Clinic